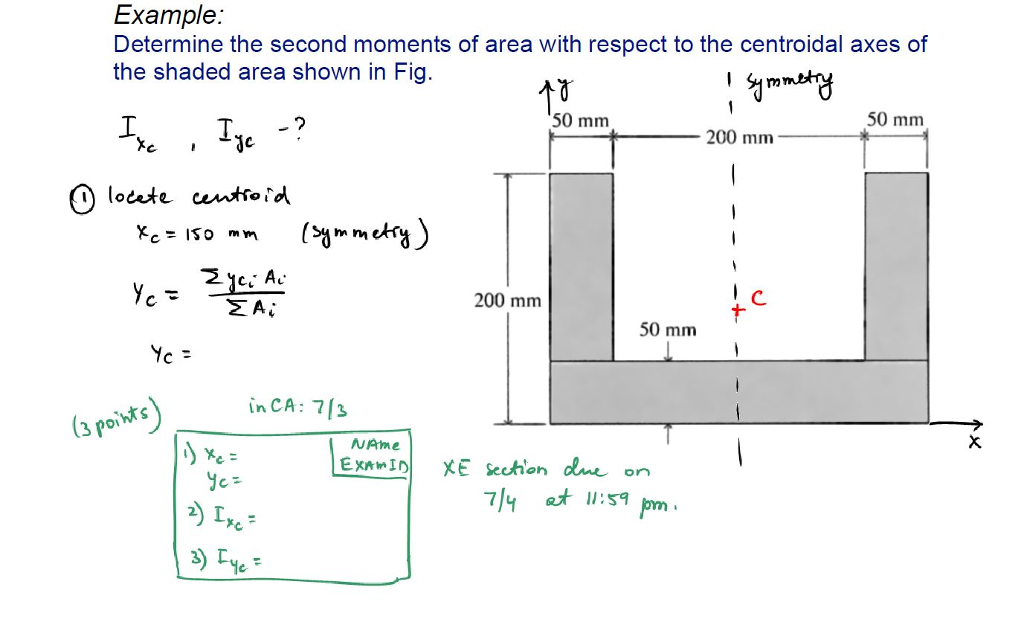
Solved Determine the second moments of area with respect to
In this video, we'll explore the concept of the second moment of area, also known as the moment of inertia, for rectangular cross section beams. We'll start.
Solved how to calculate the second moment of area intertia
For a layer of thickness δ y a distance y from the neutral axis, which passes through the centroid, the second moment of area for the layer is: Second moment of area of strip = y 2 δ A = y 2 b δ y. The total second moment of area for the section is thus: (5.4.11) Second moment of area = ∫ − d / 2 d / 2 y 2 b dy = b d 3 12.

Second moment of area YouTube
Topic: Area Moment of Inertia Here, you can learn what an area moment of inertia (also known as second moment of area, or second-order area moment) is, where it finds application in engineering mechanics, and how to calculate it. Let's explore these essential concepts together.
.png)
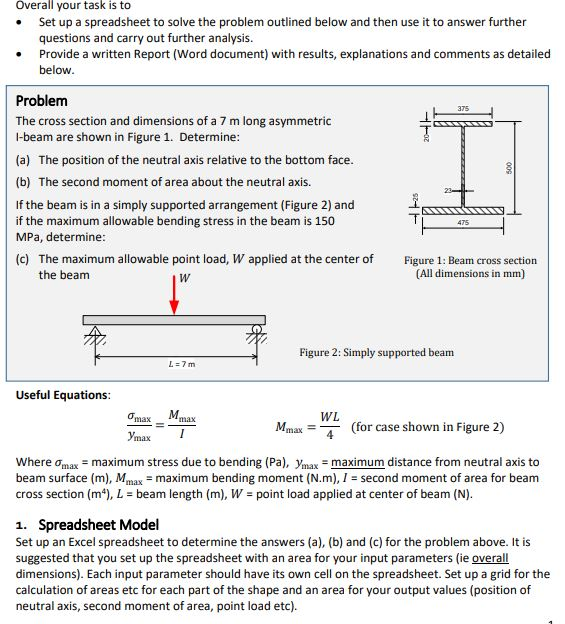
[Solved] For each section illustrated, find the se SolutionInn
To calculate the second moment of area, also known as the area moment of inertia, you integrate the area of the section times the square of the distance from an axis. For a rectangular section, it can be calculated using the formula I = b*h^3/12 for the axis through the centroid.

Statics Second Moment of Areas 2 YouTube
The second moment of area is a geometric property. If we change the material type or grade, the second moment of area DOES NOT change. As we've already mentioned, the second moment of area has dimensions of length to the fourth power, L 4 L^4 L 4. 3.0 Geometric Axes and Sign Conventions
Review Exercise Second Moment of Area TU Delft OCW
The second moment of area or second moment of inertia is a property of two-dimensional shapes. One of its main applications is describing the behaviour of beams, how they will bend given the load applied or describing buckling of columns. In these cases, the two-dimensional shape is the cross-section of the beam or column.
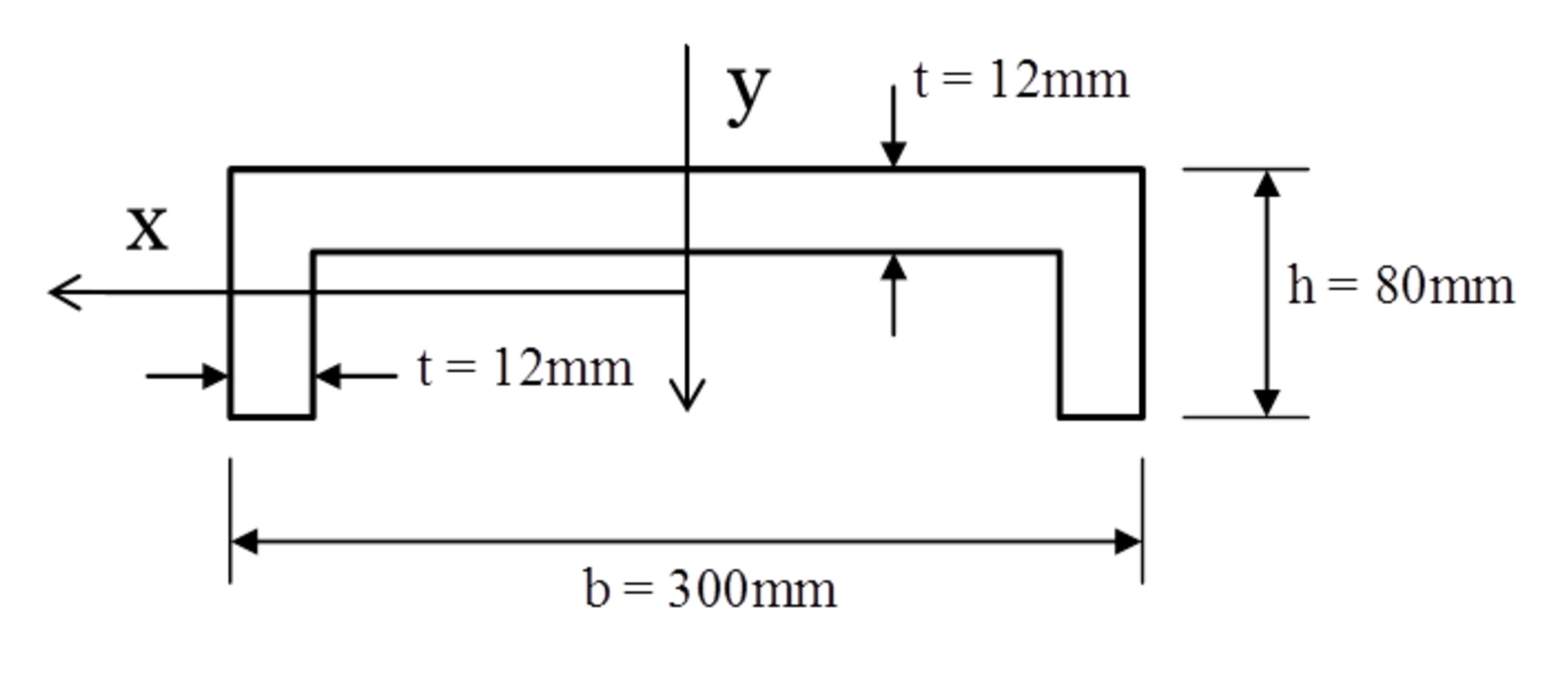
Second Moment Of Area Beam Cross Section The Best Picture Of Beam
The Product Moment of Inertia is, by definition, zero for principal axes. Elastic Section Moduli: The elastic section moduli are equal to the second moments of area / moments of inertia divided by the distance to the farthest fibre in the cross-section perpendicular to the axis of bending. Values are provided for both positive and negative.

Introduction to Second Moment of Area YouTube
The area moment of inertia is a property of a two-dimensional plane shape which characterizes its deflection under loading. It is also known as the second moment of area or second moment of inertia. The area moment of inertia has dimensions of length to the fourth power. Unfortunately, in engineering contexts, the area moment of inertia is often called simply "the" moment of inertia even.
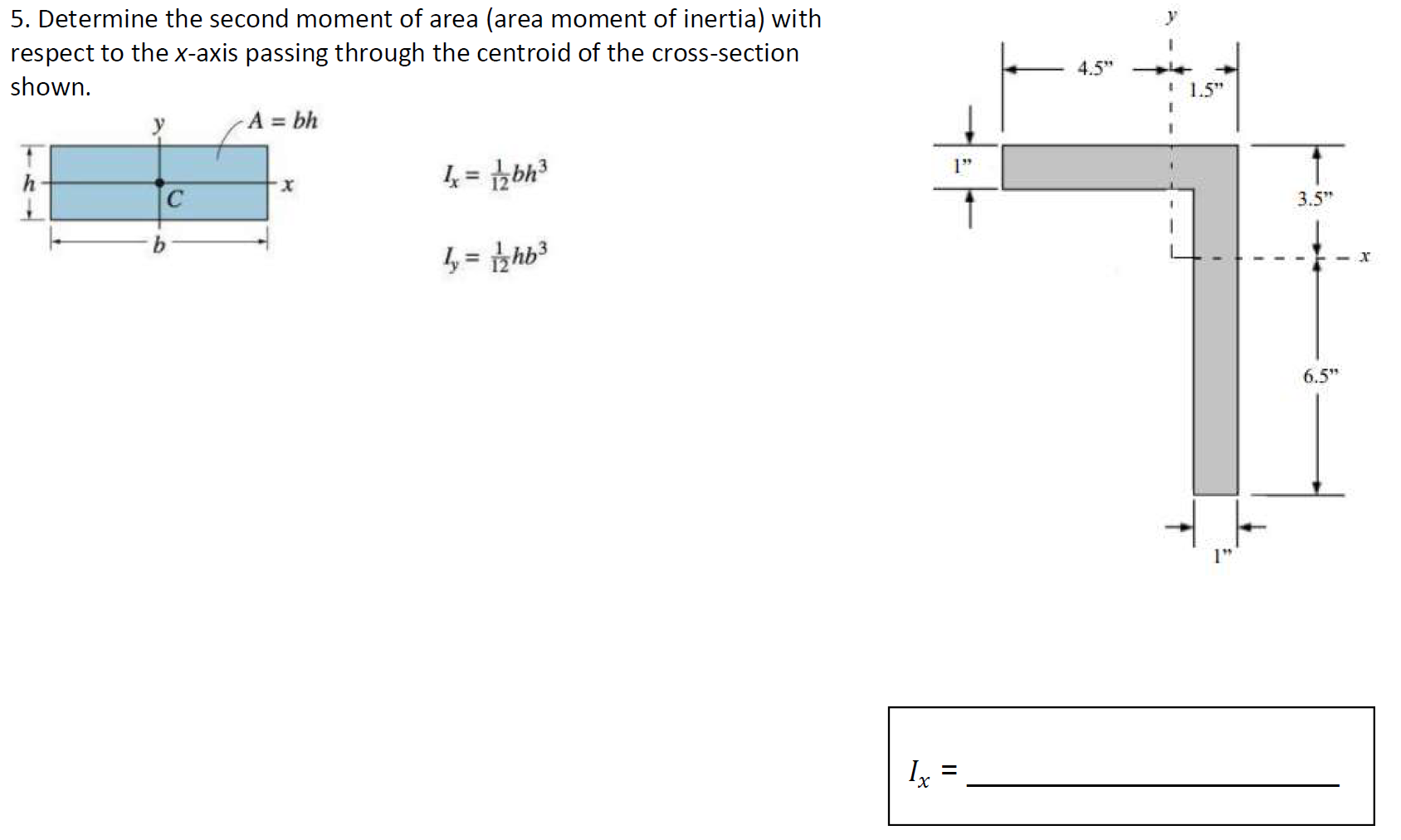
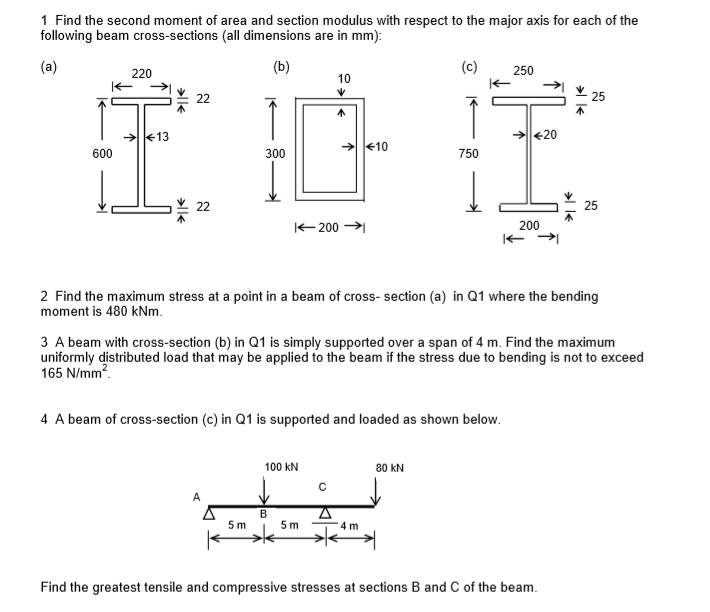
Solved 5. Determine the second moment of area (area moment
First and Second Moment of Area. Moment in Physics. In Physics Moment (or Torque) is force times distance: But there are other Moments, read on! First Moment of Area. First Moment of Area is area times distance (to some reference line): First Moment of Area = A x d. For this simple case we can multiply the whole area by the distance (from its.

Second Moment of Area Calculation for Simple Symmetrical Shapes Example 3 YouTube
Area Moment of Inertia or Moment of Inertia for an Area - also known as Second Moment of Area - I, is a property of shape that is used to predict deflection, bending and stress in beams.. Area Moment of Inertia - Imperial units. inches 4; Area Moment of Inertia - Metric units. mm 4; cm 4; m 4; Converting between Units. 1 cm 4 = 10-8 m 4 = 10 4 mm 4; 1 in 4 = 4.16x10 5 mm 4 = 41.6 cm 4.
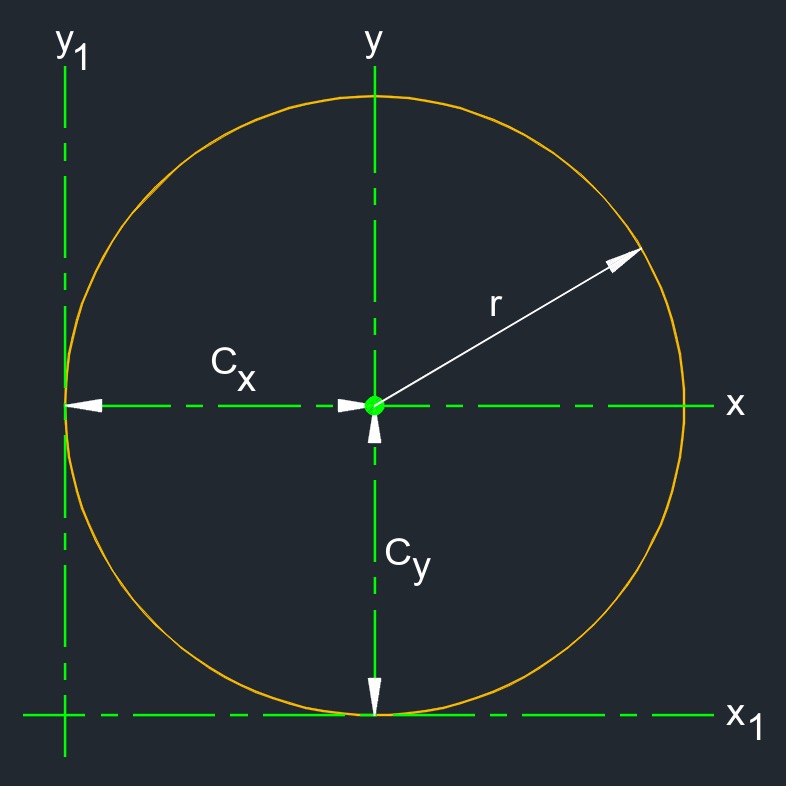
Second Moment of Area of a Circle
This free multi-purpose calculator is taken from our full suite Structural Analysis Software. It allows you to: Calculate the Moment of Inertia (I) of a beam section (Second Moment of Area) Centroid Calculator used to calculate the Centroid (C) in the X and Y axis of a beam section. Calculate the First moment of area (Statical Moment of Inertia.

How to calculate the neutral axis and the second moment of area on T shape of beam, cross
How to calculate Second Moment of Area| Detailed explanation. Video explains moment of area of different section and its real life applicationComplete Lectur.

Class 24 Structures Second Moment of Areas YouTube
Moment of Inertia calculators. Here is a list of the available calculation tools relative to the moment of inertia of a shape. More accurately, these tools calculate the second moment of area, which is a purely geometric property of a planar shape (not related to its mass). The second moment of area is commonly used in engineering disciplines.

Solved Calculate the second moment of area of the composite
Second Moment of Area -- from Wolfram MathWorld. Geometry. Plane Geometry. Miscellaneous Plane Geometry.

Area Moments
The area moment of inertia, also called the second moment of area, is a parameter that defines how much resistance a shape (like the cross-section of a beam), has to bending because of its geometry. Consider a thin plank that supports a 100 kg load. The plank will be much less stiff when the load is placed on the longer edge of the cross-section.
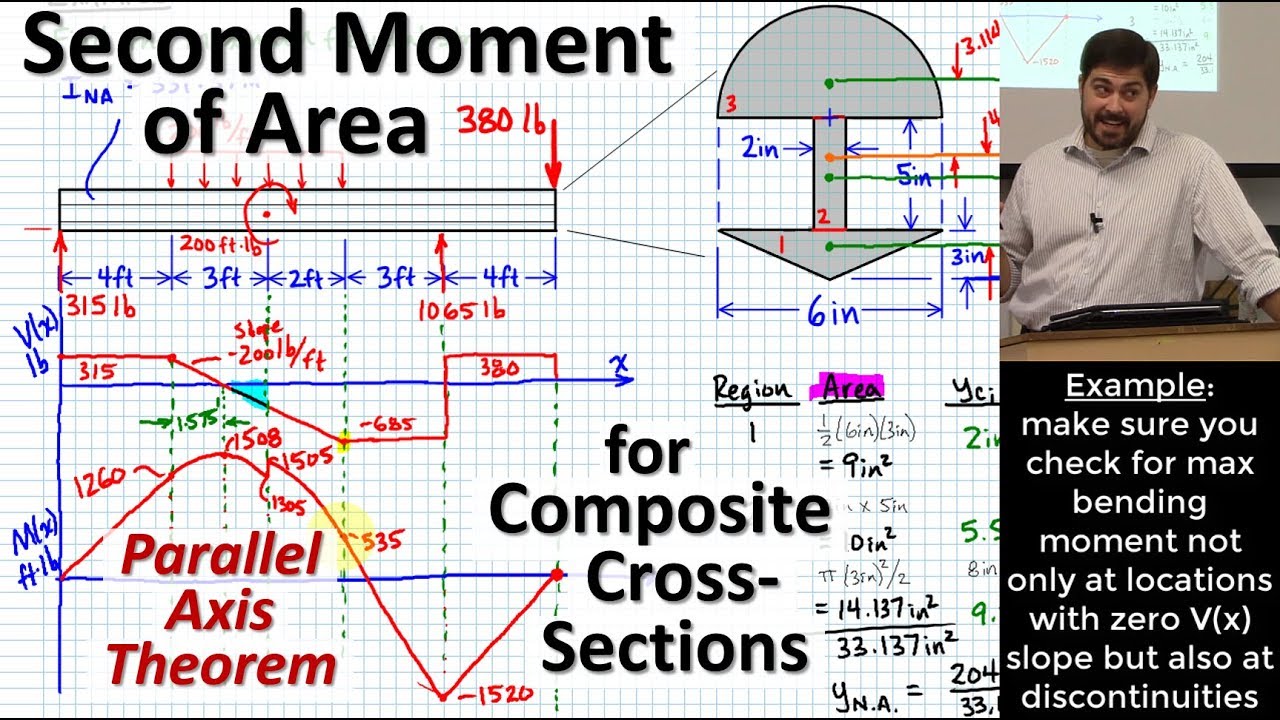
Second Moment of Area for Beams with CompositeShape CrossSections Parallel Axis Theorem (PAT
The second moment of area measures a beam's ability to resist deflection or bending over a cross-sectional area. It is also known as the area moment of inertia. The second moment of area is used to predict deflections in beams. It is denoted by *I *and is different for different cross sections, for example rectangular, circular, or cylindrical.
- Channel 9 Tennis Commentators Tonight
- Tom Holland And Dominic Sandbrook
- Map Of New South Wales Coastal Towns
- Coral Island Tree Planting Festival
- Motels Corowa New South Wales
- 10 Past 10 In Digital Time
- Cast Of Ride The High Country
- Volvo Xc90 Price Australia 2023
- Hat Head National Park Camping
- Mr And Mrs Potato Head Costumes
