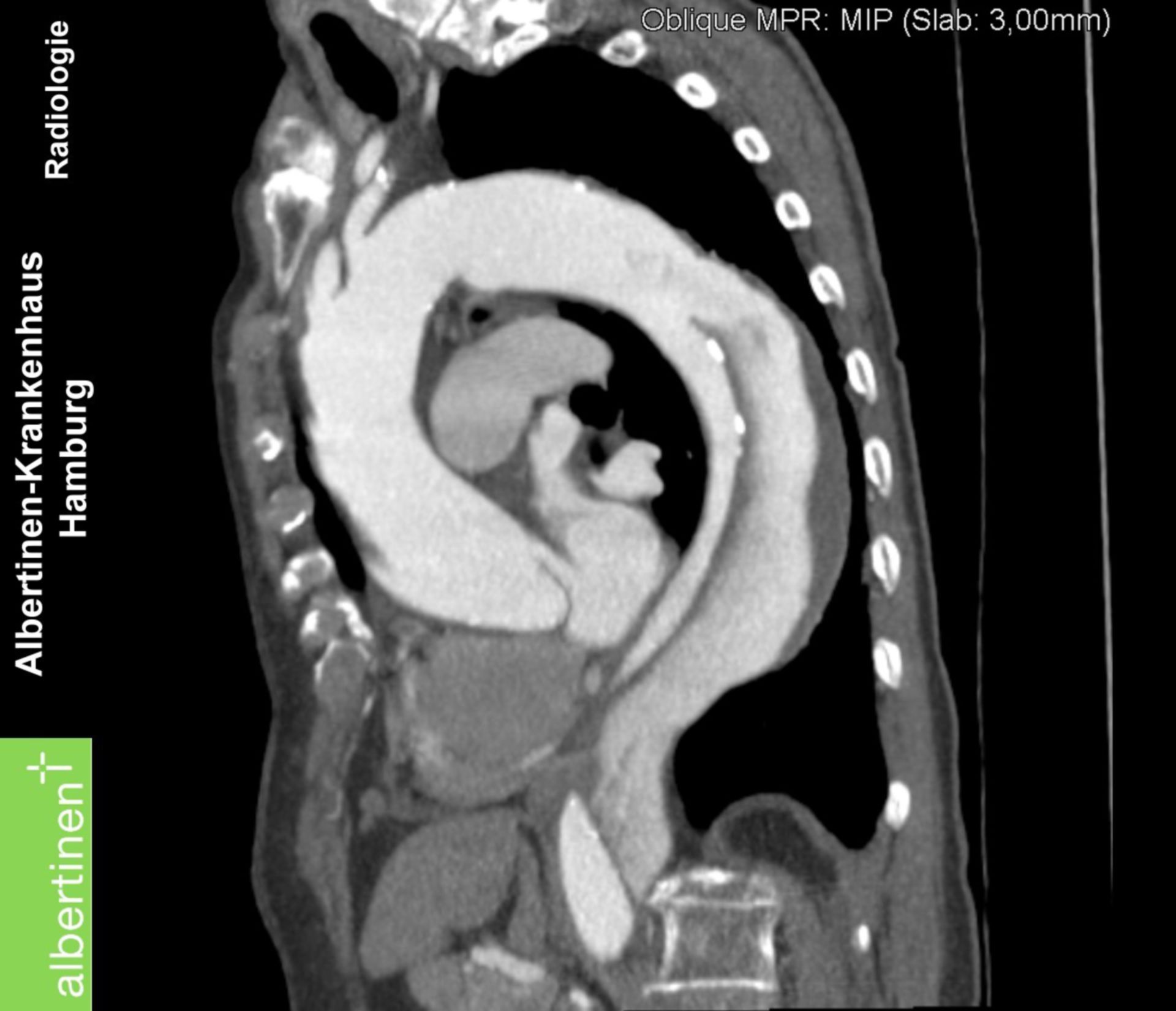
CTscan Aortic dissection, longitudinal view DocCheck
The size of a given segment of the thoracic aorta is influenced by age, sex, height, and body size. 2 Aortic z-scores and other diameter indexing methods (see Section 2.3, "Definitions of Dilation and Aneurysm of the Aortic Root and Ascending Thoracic Aorta") may assist with risk assessment. 3 Of all TAA, aneurysms of the aortic root.

Aortic arch aneurysm Radiology Case
Unfolding of the aortic arch. Cardiac size is within normal limits. Anterior wedging of T12 is noted, with near complete height loss. Degeneration of the AC joints. Case Discussion Unfolded aortic arch. 1 article features images from this case. Unfolded aorta; 2 public playlists include this case.
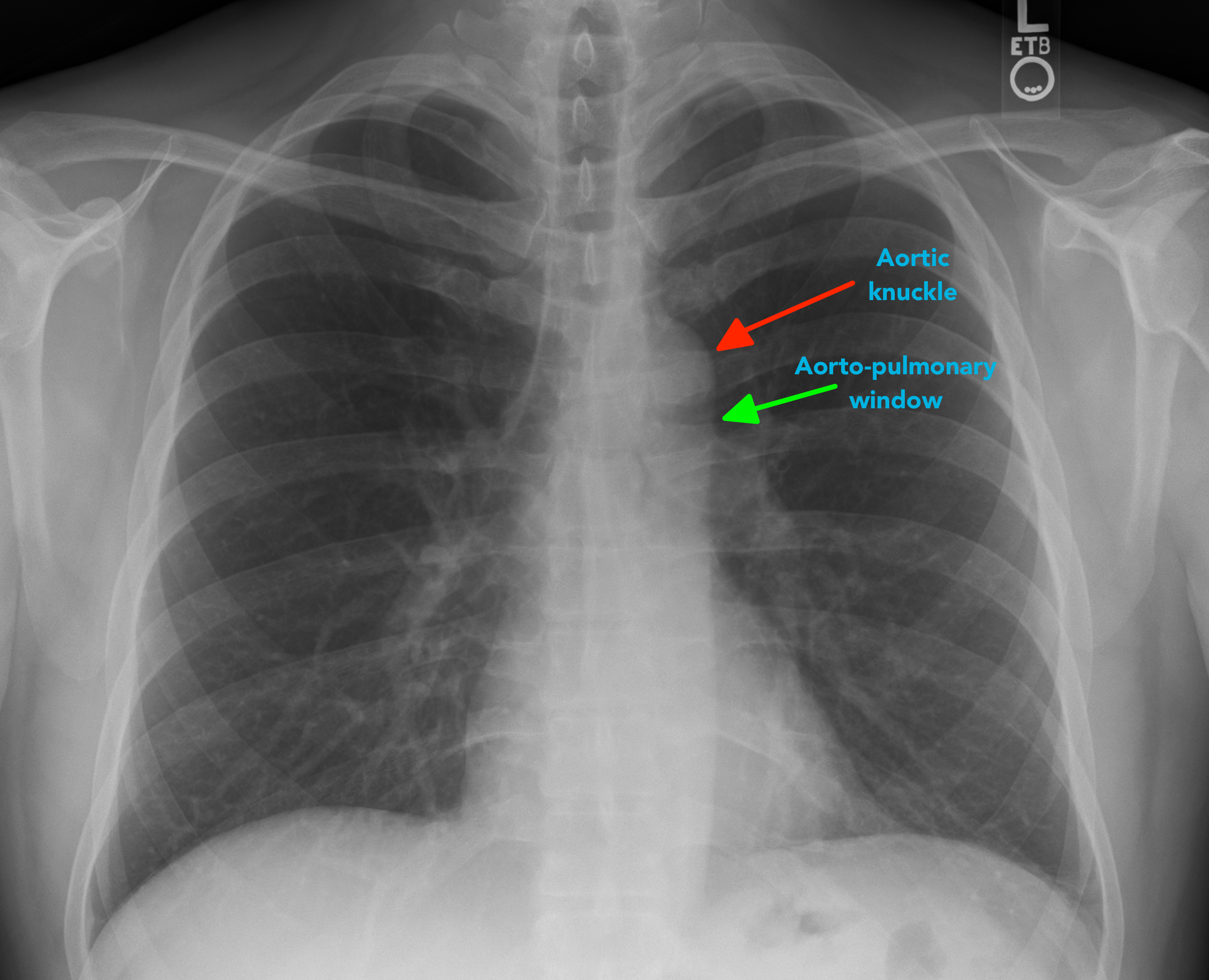
Chest Xray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology OSCE
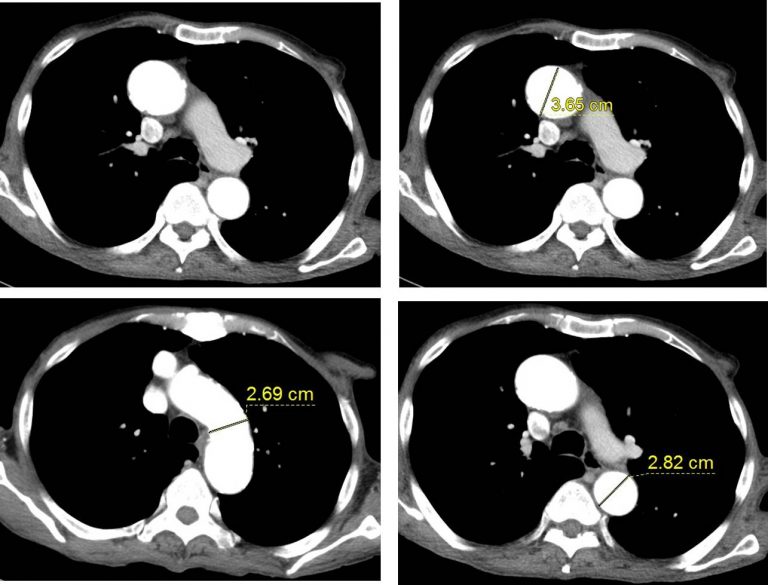
Measuring Aortic Unfolding using Non-contrast Cardiac CT. Aortic unfolding was defined as the longest distance between the ascending and descending aortas, including the aortic lumen and aortic wall, on a selected CT slice at the level of the pulmonary artery bifurcation (Fig. 1). Two radiologists who were blind to the clinical information.

Dilated aorta with unfolding of arch on Xray chest PA view All About Cardiovascular System
In this article, we'll look into the role of the thoracic aorta, what thoracic aortic ectasia means, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and prevention. Understanding the Thoracic Aorta. The thoracic aorta is a large, vital blood vessel originating from the heart's left ventricle, specifically the aortic valve.
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Clinical Features Management TeachMeSurgery
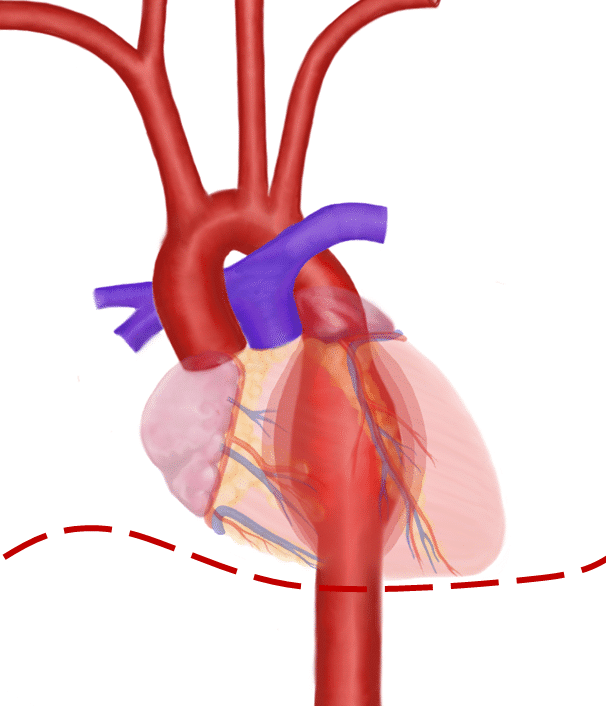
Radiological studies have shown that the thoracic aorta becomes tortuous, enlarged and unfolded with aging and disease. 10, 11 Unfolding may change the alignment between the oesophagus and descending aorta, because the descending part moves left laterally and then curves back to exit the thorax. Therefore, unfolding may also change the.

Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Circulation
The term unfolded aorta refers to the widened and decreased curvature of the aortic arch on a frontal chest radiograph giving an 'opened up' appearance. It is one of the more common causes of apparent mediastinal widening and is seen with increasing age, usually associated with aortic calcification. It occurs due to the discrepancy in the.
Unfolded aorta Radiology Cases
Aortic unfolding measurement. Transaxial slice at the pulmonary artery bifurcation from a coronary artery calcium scan showing the method for deriving the aortic unfolding. The white line represents the farthest distance from the ascending aorta to the descending aorta at the level of the pulmonary artery bifurcation.
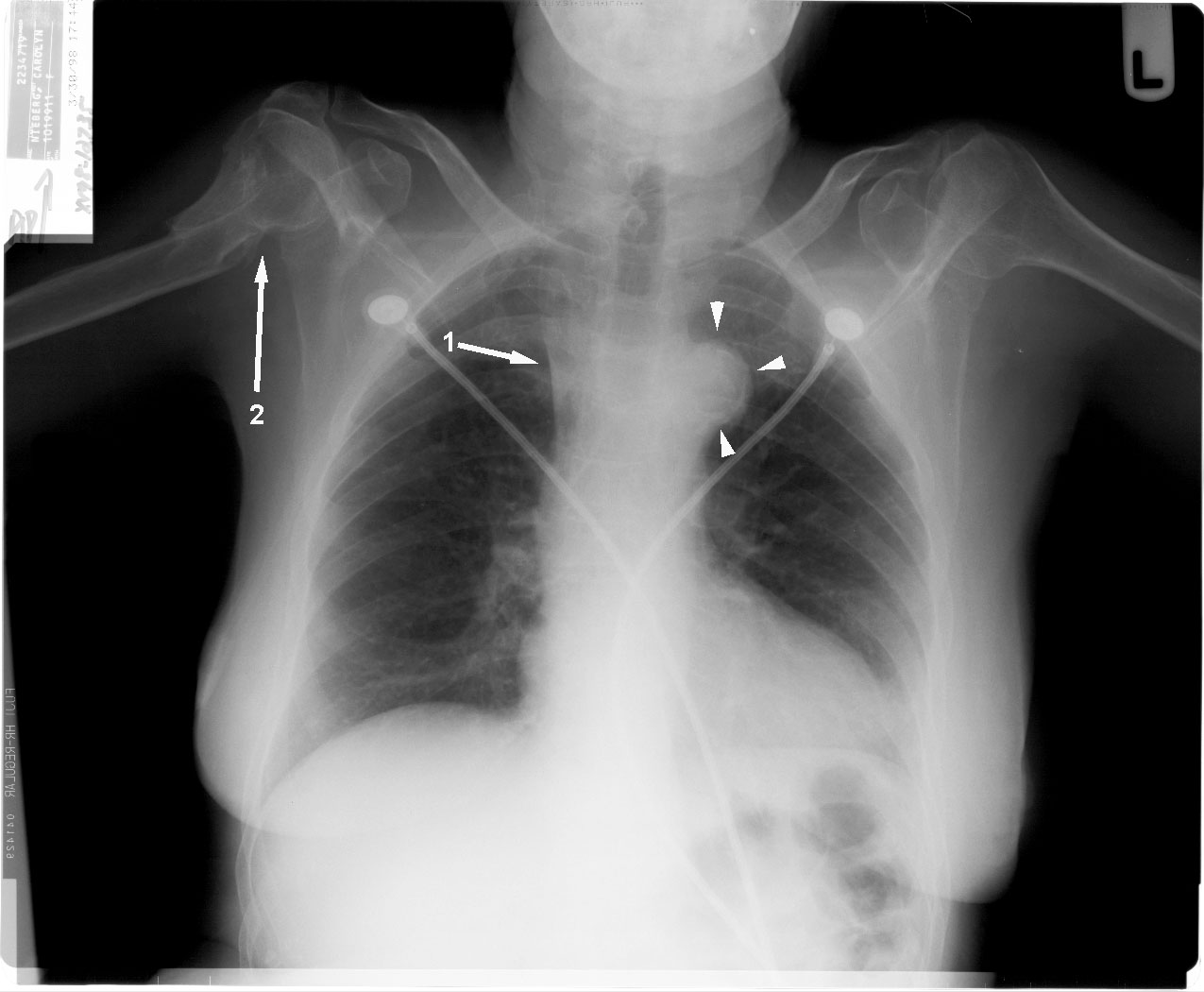
MasterMedFacts Chest XRay
Unfolded aorta. An unfolded aorta is a radiological finding which is commonly seen in older people. The chest radiograph shows slight lengthening of the thoracic aorta resulting in some tortuosity. It is not significant, but should not be confused with other sinister causes of mediastinal widening.

CT Appearance of Thoracic Aortic Graft Complications AJR
Aortic unfolding is an abnormality visible on a chest X-ray, that shows widening of the mediastinum which may mimic the appearance of a thoracic aortic aneurysm. [1] With aging, the ascending portion of the thoracic aorta increases in length by approximately 12% per decade, whereas the diameter increases by just 3% per decade.

Image Predictors of Treatment after Thoracic Aortic Dissection Repair RadioGraphics
Stroke symptoms, including weakness or paralysis on one side of your body, trouble talking. Aortic dissection is life-threatening. About 40% of patients die immediately from complete rupture and bleeding out from the aorta. The risk of dying can be as high as 1% to 3% per hour until the patient gets treatment.

Unfolded aorta Radiology Cases
The thoracic aorta (TA) is subject to progressive size increase and a concomitant unfolding process. 1, 2, 3 The noninvasive assessment of TA geometry was employed to better predict aneurisms.

Serial CT sections that demonstrate unfolding of the thoracic aorta... Download Scientific Diagram
Thoracic aortic aneurysms are often found when an imaging test is done for a different reason. If you have symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm, your health care provider may ask about your family's medical history. Some aneurysms can run in families. Tests. Imaging tests can be used to confirm or screen for a thoracic aortic aneurysm.

Chest Xray reveals unfolding of aorta, hazy right para Openi
MRI also allows the assessment of the whole thoracic aorta geometry in 2D sagittal oblique planes acquired using black-blood spin echo or steady-state free precession sequences,. Taken together, these findings suggest that AA dilation and lengthening, resulting in aortic unfolding and the augmentation of proximal aortic volume, may help to.
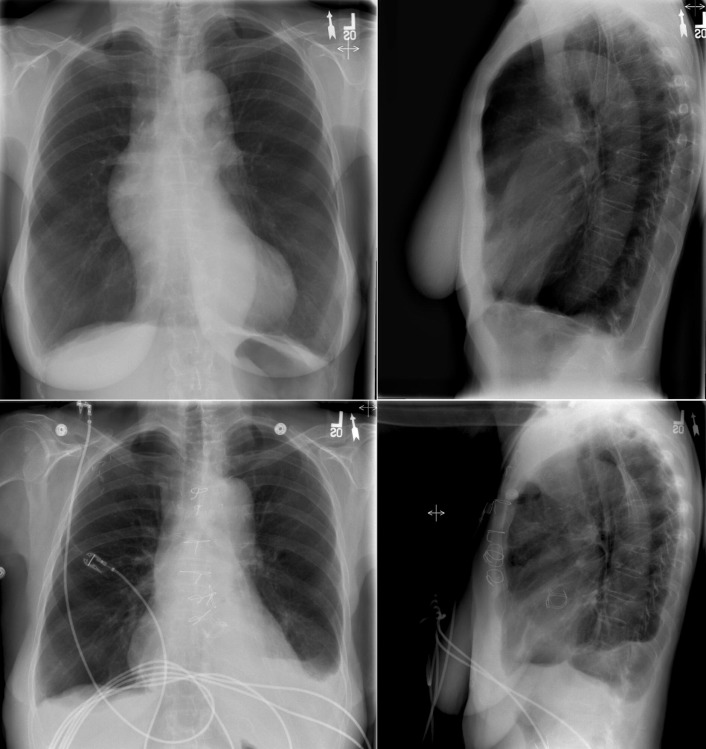
The Thoracic Aorta Radiology Key
Eliason: During an abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture, an individual typically experiences severe abdominal or back pain. Sudden death can also occur. In some cases, patients might experience symptoms without a rupture. These patients may get a warning of abdominal pain or escalating back pain. If the aneurysm is in the chest only, the.
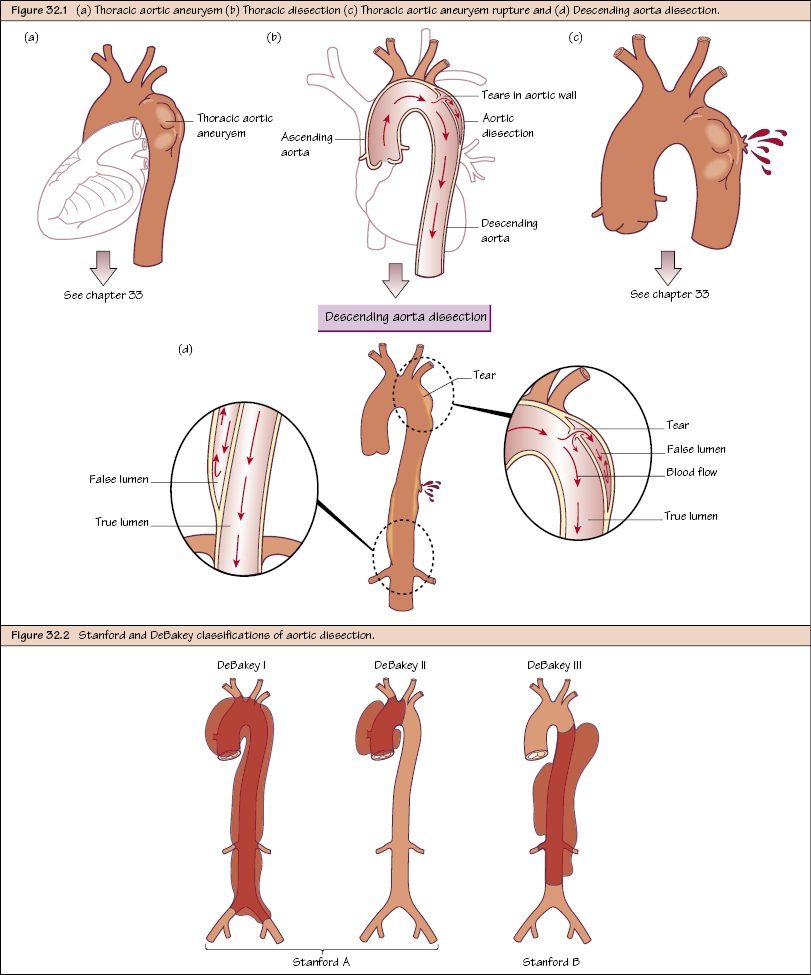
Thoracic Aortic Disease I Dissection Thoracic Key
The thoracic aorta is responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to multiple structures, including the head, neck, upper extremities, and thoracic structures. The aorta is the largest vessel within the human body. It originates from the left ventricle of the heart anterior to the pulmonary artery before arching posteriorly and descending along.

Dilated aorta with unfolding of arch on Xray chest PA view All About Cardiovascular System
The term unfolded aorta refers to the widened and decreased curvature of the aortic arch on a frontal chest radiograph giving an 'opened up' appearance. It is one of the more common causes of apparent mediastinal widening and is seen with increasing age, usually associated with aortic calcification.. It occurs due to the discrepancy in the growth of the ascending aorta with age, where the.
- Coat Of Arms Australia Meaning
- How Many Calories In 1 Tbsp Butter
- Black And White American Staffy
- Main Cherry Cellar Door
- Elite Body Contouring Near Me
- Swan Valley River Cruise Lunch
- French Puff Pastry Biscuits In A Heart Shape
- How To Write Us Dollars
- House For Sale In North Melbourne
- Jess Glynne On The Voice
