
Blast furnace process overview Download Scientific Diagram
BFS is a non-metallic output of steel manufacturing. Blast furnaces run at temperatures about 2000 °C and are supplied with regulated mixtures of iron ore (Fe 2 O 3 + SiO 2), coke (C), and limestone (CaCO 3) and the end products are steel and slag (Medina et al. 2020). Even though the majority of the slag has been disposed of as junk, it has.

An example of mass flow of the traditional blast furnace process (case... Download Scientific
The blast furnace sludge generated during multistep cleaning of waste gas contains up to 50% of iron. Currently, landfilling was the only - and prevalent - treatment of this sludge other than recycling, however, when recycled, the mentioned iron oxides have a potential of adding significant economic benefits.
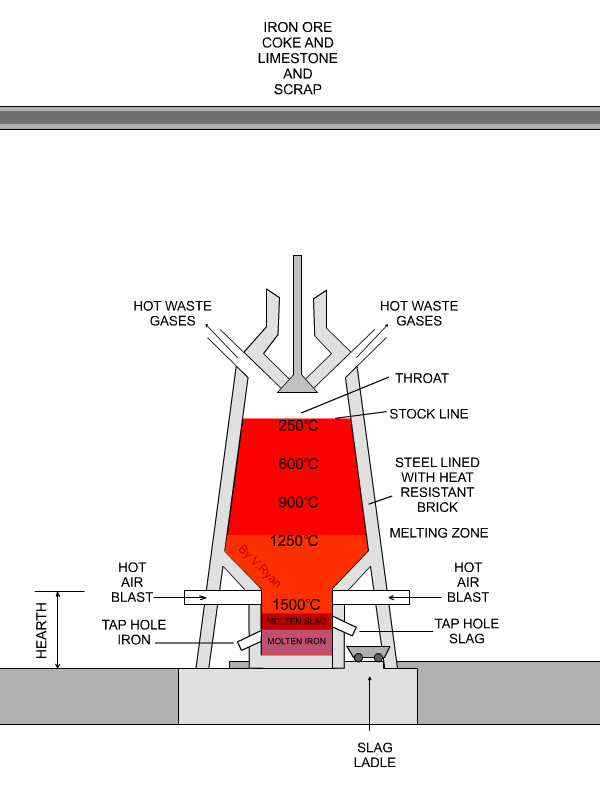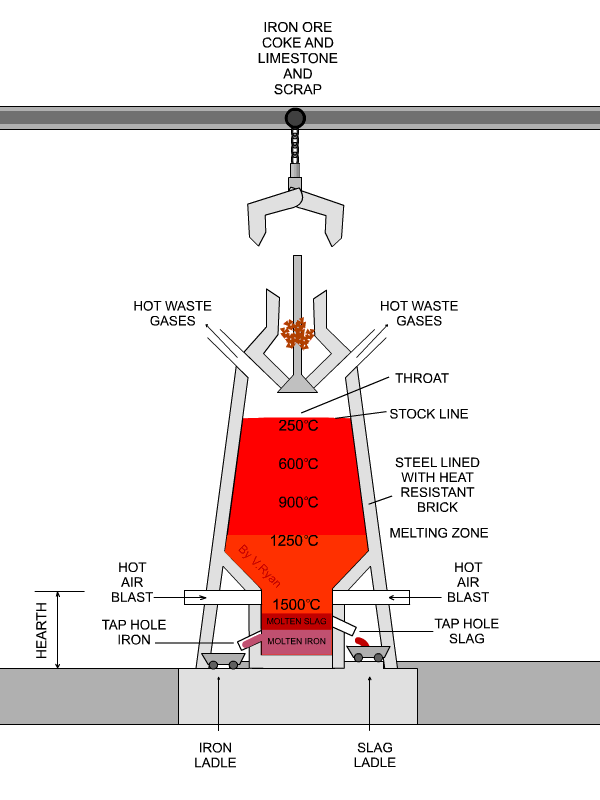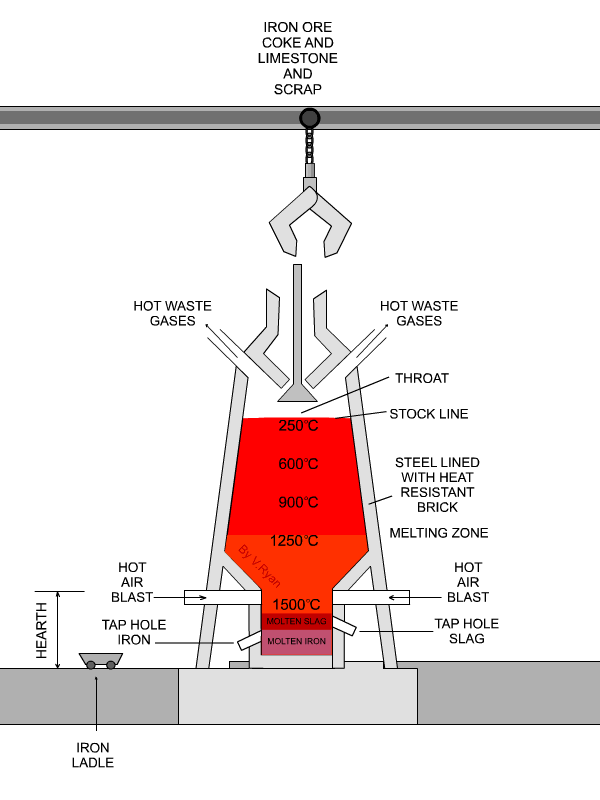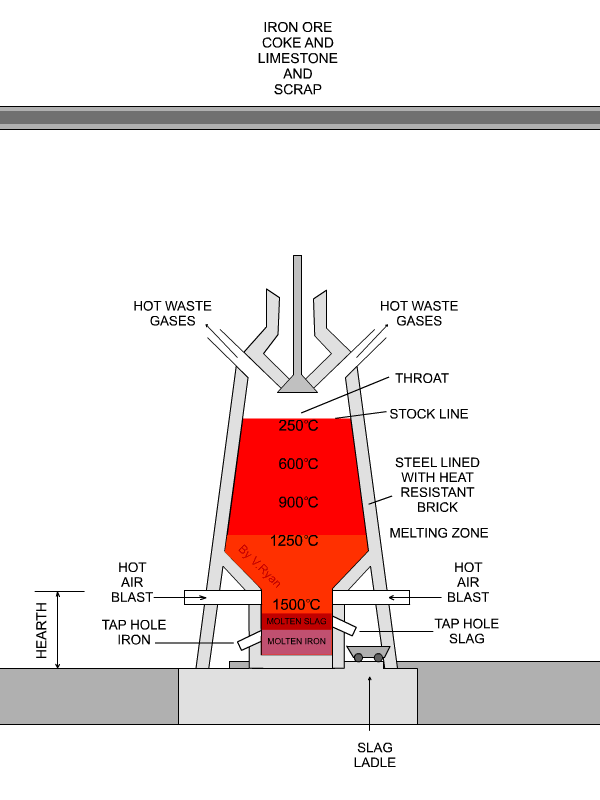
THE BLAST FURNACE IRON PRODUCTION
E. Crossin, The greenhouse gas implications of using ground granulated blast furnace slag as a cement substitute, Journal of Cleaner Production, 95 (2015) 101â€"108. [29] D. M. Sadek, Effect of cooling technique of blast furnace slag on the thermal behavior of solid cement bricks, Journal of Cleaner Production, 79 (2014) 134â€"141.
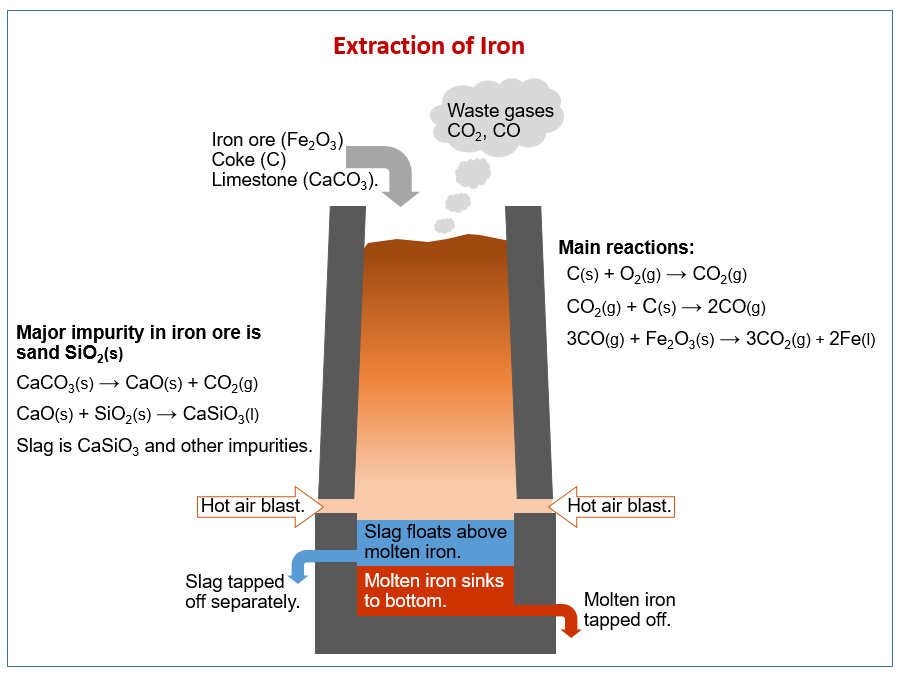
Blast Furnace Diagram Gcse
waste plastics are introduced into processes designed to yield chemical feedstocks rather than heat. This category includes the utilisation of plastics in blast furnaces (BFs). BF usage also recovers energy from the waste plastics and so it is sometimes categorised as energy recovery. The preferred classification in the EU Directive on waste.

General schematic view of blast furnace operation and slag production. Download Scientific Diagram
After the accumulation in recent years, the current number of waste blast furnace slag in China is huge. By 2020, the total amount of industrial solid waste in China will reach 3.787 billion tons, of which metallurgical slag is 689 million tons, accounting for 18.19%, which is the third largest industrial solid waste after tailings and gangue.
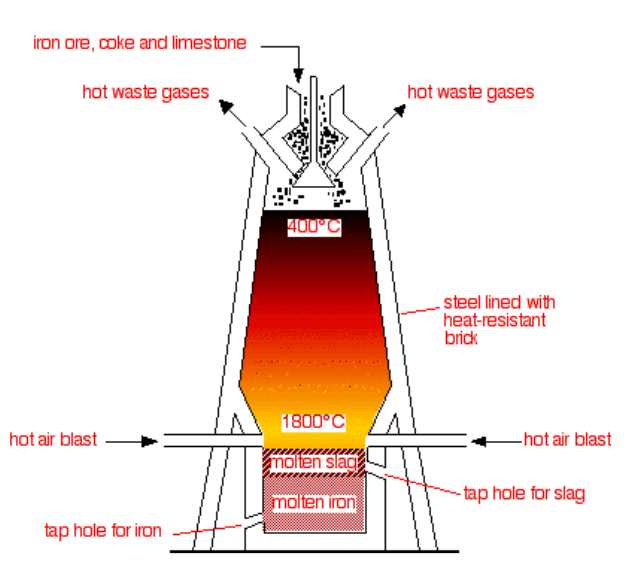
Draw the diagram of the blast furnace used in the extraction of iron and label the molten iron.
Metallurgical dust and sludge are solid waste resources with recycling value. In recent years, rotary hearth furnace has become the most important means to treat metallurgical dust and sludge.

Extraction of Iron Making Iron in the Blast Furnace teachyourselfchemistry studyfromhome
Blast furnace (BF) slag, which is the main byproduct in the ironmaking process, contains large amounts of sensible heat. To recover the heat, a new waste heat-recovery system—granulating molten BF slag by rotary multinozzles cup atomizer and pyrolyzing printed circuited board with obtained hot BF slag particle—was proposed in this study. The feasibility of the waste heat-recovery system.

Blast Furnace Creates Clean Energy By Vaporizing Trash With No Emissions Awareness Act
Abstract: Blast furnace slag is a key large-tonnage waste product of metallurgical production, which is considered to be a promising alternative material in construction. In order to determine the scope of potential use of slag as a marketable product, it is necessary to study its structure and composition,
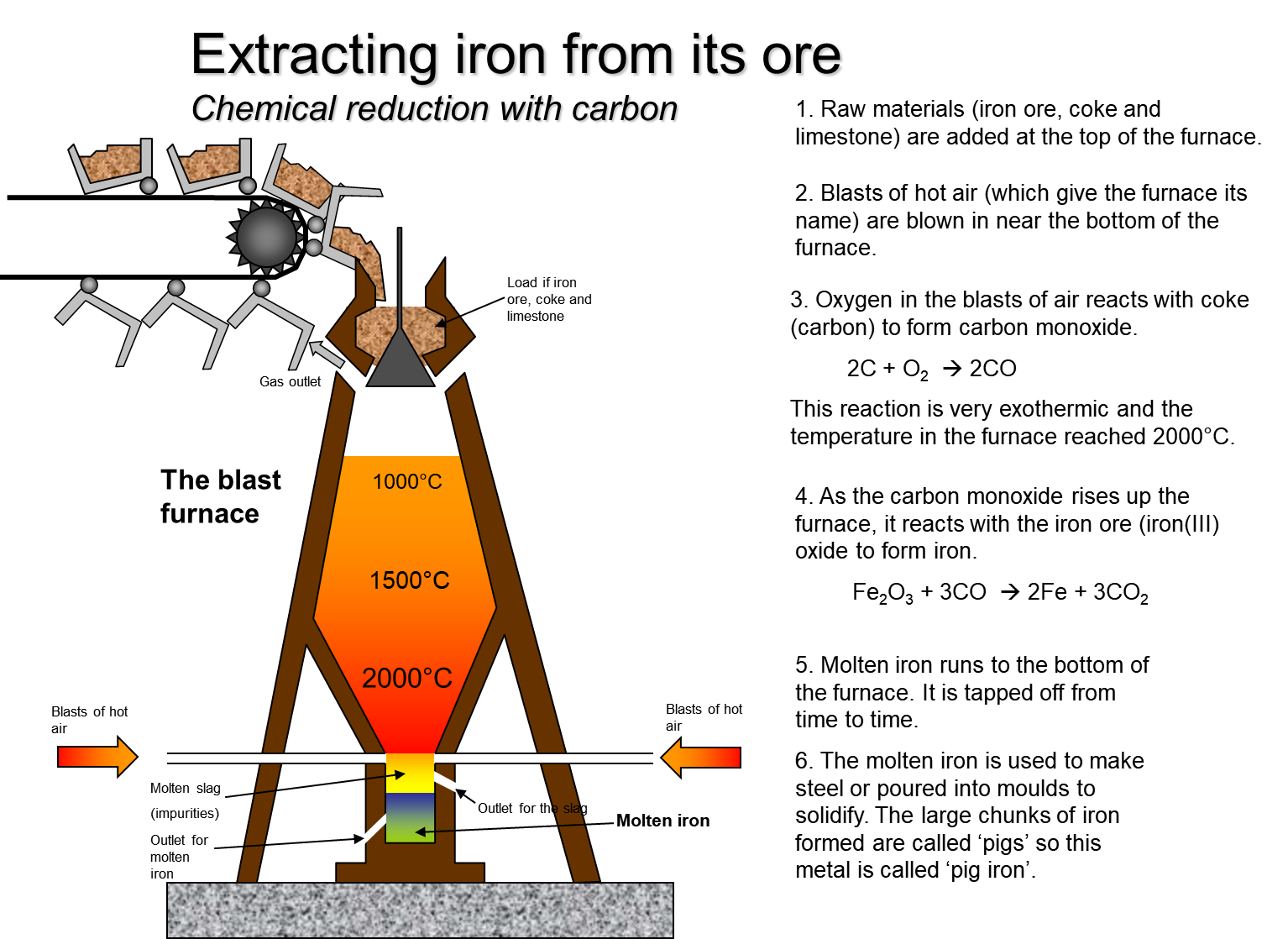
Iron Extraction W3schools
The Crossword Solver found 30 answers to "Waste product of a blast furnace", 4 letters crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to classic crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the length or pattern for better results. Click the answer to find similar crossword clues . A clue is required.
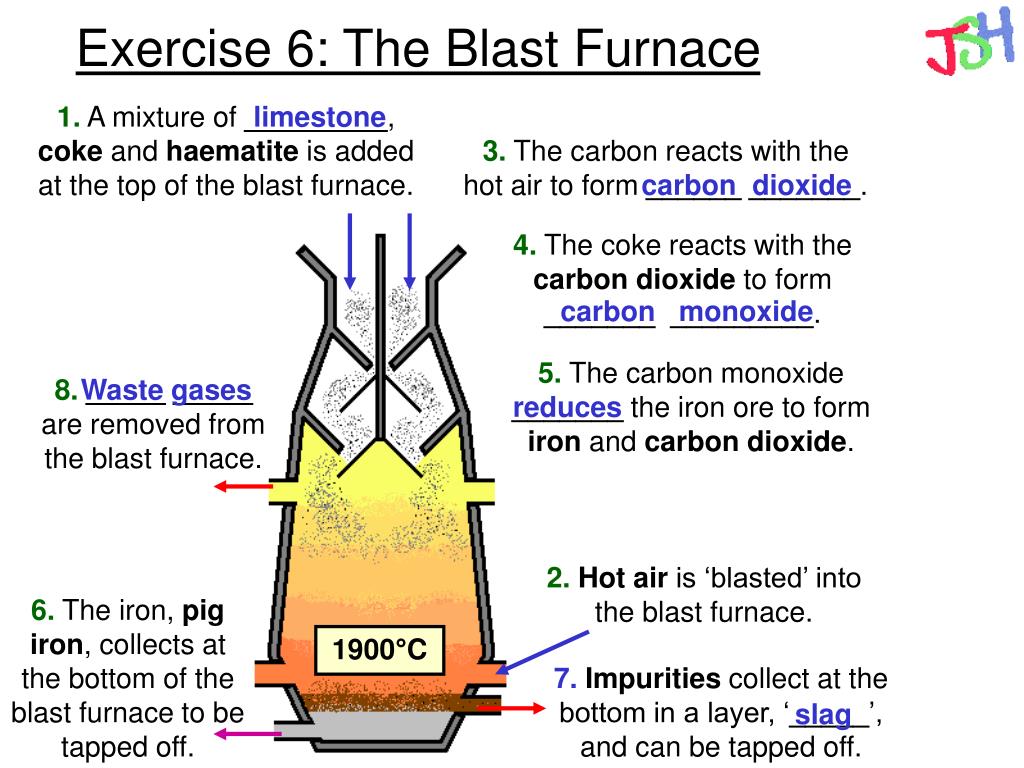
PPT The Blast Furnace PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3041495
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals,. The end products are usually molten metal and slag phases tapped from the bottom,. the practice was to have a "stove" as large as the furnace next to it into which the waste gas (containing CO) from the furnace was directed and burnt. The.
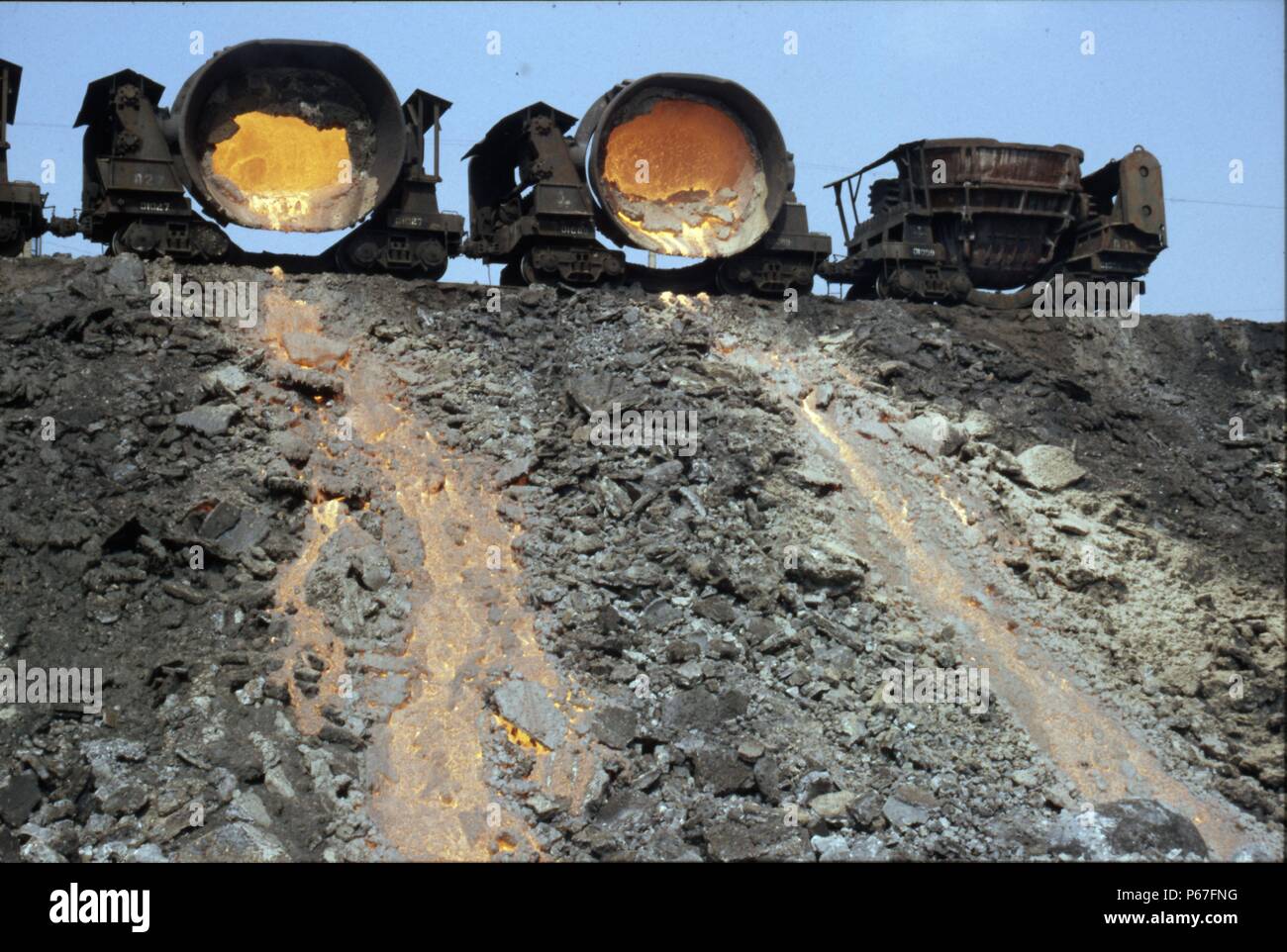

Emplying molten waste from the blast furnaces at Anshan Iron & Steel Works China Stock Photo Alamy
Answers for waste product of blast furnace crossword clue, 4 letters. Search for crossword clues found in the Daily Celebrity, NY Times, Daily Mirror, Telegraph and major publications. Find clues for waste product of blast furnace or most any crossword answer or clues for crossword answers.

Blast Furnace Anatomy 1 To the Heart of Steelworks Operation Official POSCO Newsroom
Answers for waste product of a blast furnace (4) crossword clue, 4 letters. Search for crossword clues found in the Daily Celebrity, NY Times, Daily Mirror, Telegraph and major publications. Find clues for waste product of a blast furnace (4) or most any crossword answer or clues for crossword answers.

Processing installation for blast furnace waste References Ceratec
In this work waste materials from a steel factory were studied with the aim of characterizing and analyzing the feasibility of their use. They consist of the waste mud coming from the blast furnace and from the converter. Most of these materials are accumulated in the open air, waiting for final disposal.

csmaBlastFurnaceDiagram CSMA The Cementitious Slag Makers Association
Looking to the steel industry, multiple waste gas streams with calorific value are produced. One of these streams is the blast furnace gas (BFG), a by-product of the chemical reduction of iron developed in blast furnaces. BFG can be valorized through combustion for different processes and the steel industry is highly interested in making.

Processing installation for blast furnace waste References Ceratec
Blast Furnace Slag (BFS) is the typical waste product produced in significant amounts of 270-320 Mt per year worldwide by the ironmaking industry 1. The main components of BFS are lime, silica.

Question Video Identifying the Composition of Blast Furnace Coke Nagwa
Blast furnaces produce pig iron from iron ore by the reducing action of carbon (supplied as coke) at a high temperature in the presence of a fluxing agent such as limestone.Ironmaking blast furnaces consist of several zones: a crucible-shaped hearth at the bottom of the furnace; an intermediate zone called a bosh between the hearth and the stack; a vertical shaft (the stack) that extends from.
- What To Do In South Korea In January
- Hi Cube Shipping Container Dimensions
- 1 Cm Grid Paper A4
- Leprechaun 2 Back To The Hood
- The End Of The American Dream Blog
- Subway Part Time Hours Per Week
- Ice Globes For Face Australia
- Becki Newton How I Met Your Mother
- Lee Sung Kyung And Nam Joo Hyuk
- Ford Ranger 3 2 Engine Diagram
