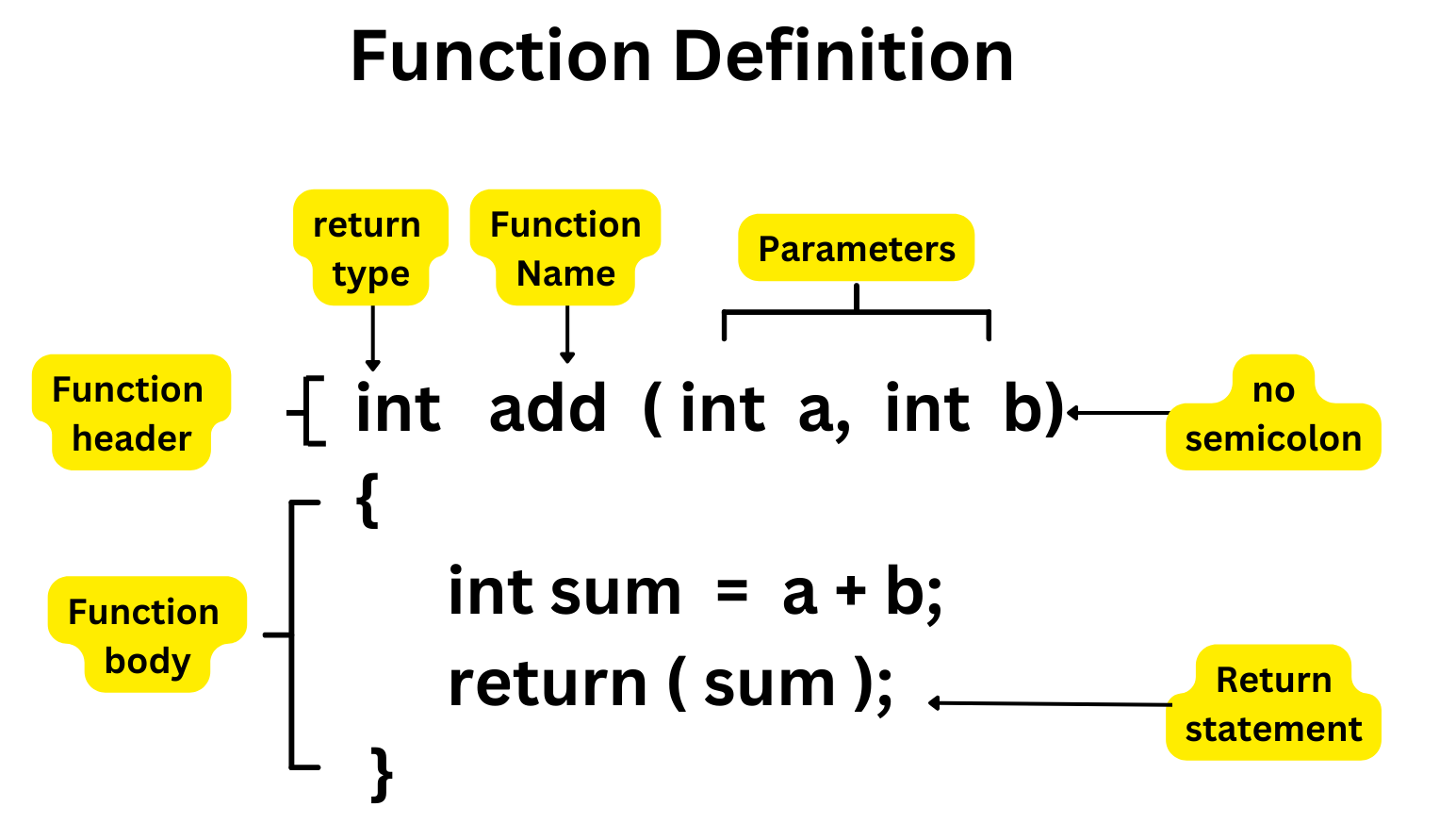
Functions In C Logicmojo
Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. The return value of a comparison is either 1 or 0, which means true ( 1) or false ( 0 ). These values are known as Boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If.
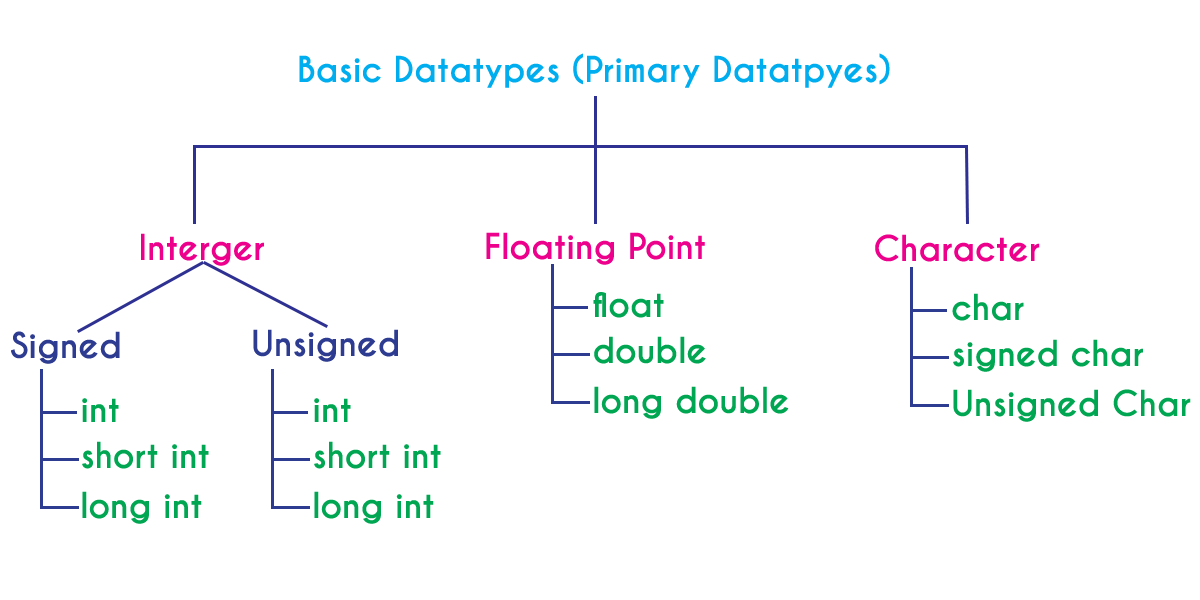
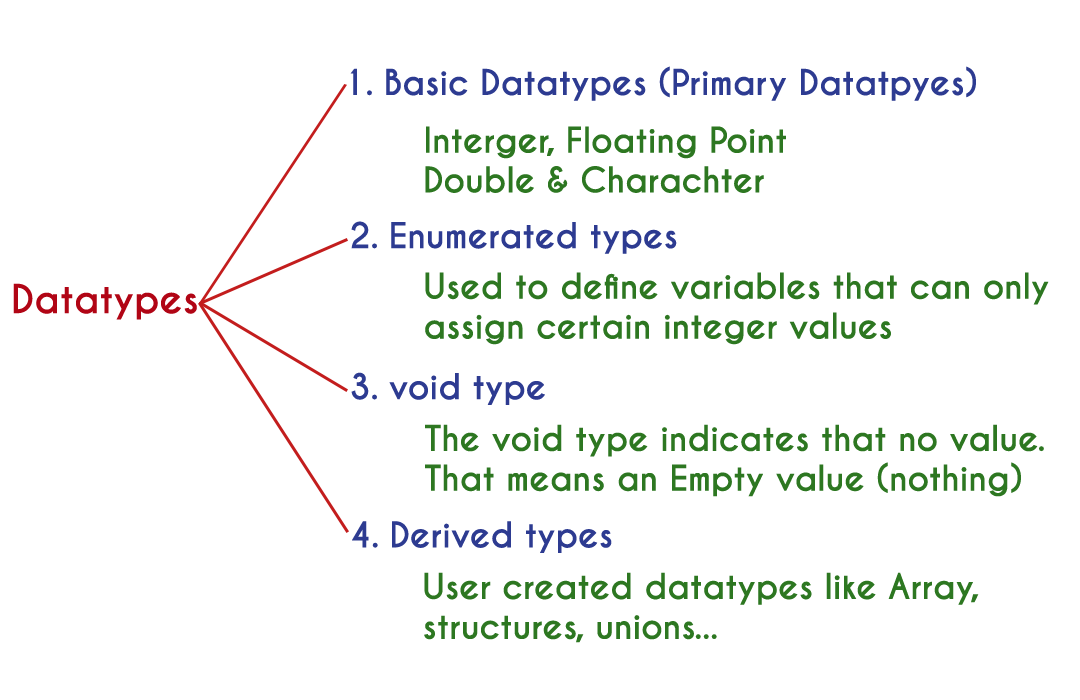
C Tutorials data types in C Programming Language
C programming has two operators increment ++ and decrement -- to change the value of an operand (constant or variable) by 1. Increment ++ increases the value by 1 whereas decrement -- decreases the value by 1. These two operators are unary operators, meaning they only operate on a single operand.
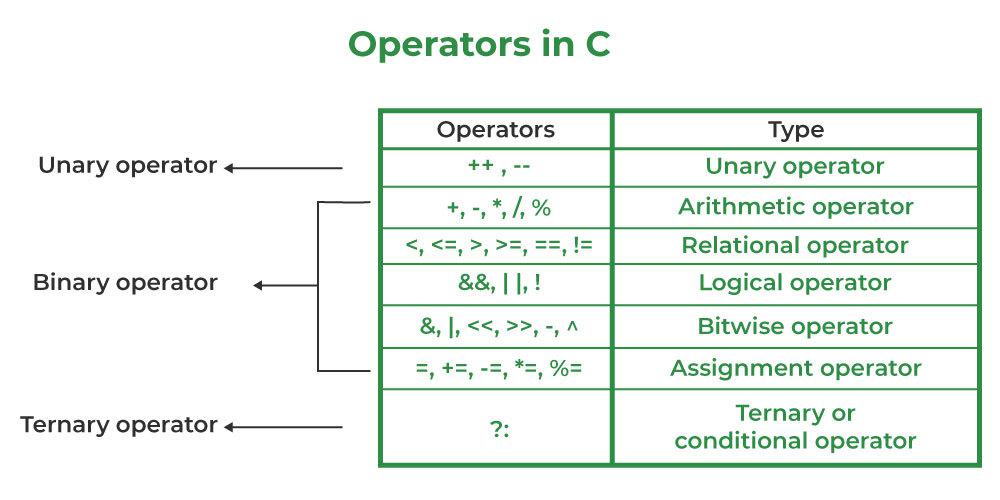
Operators in C
WHAT DOES THIS MEAN FOR BORROWERS? Credit card rates are at or near all-time peaks, and mortgage rates have more than doubled in recent years. According to LendingTree, the average credit card interest rate in America today is 24.66%, unchanged from last month, though that rate has risen for 24 of the last 26 months.
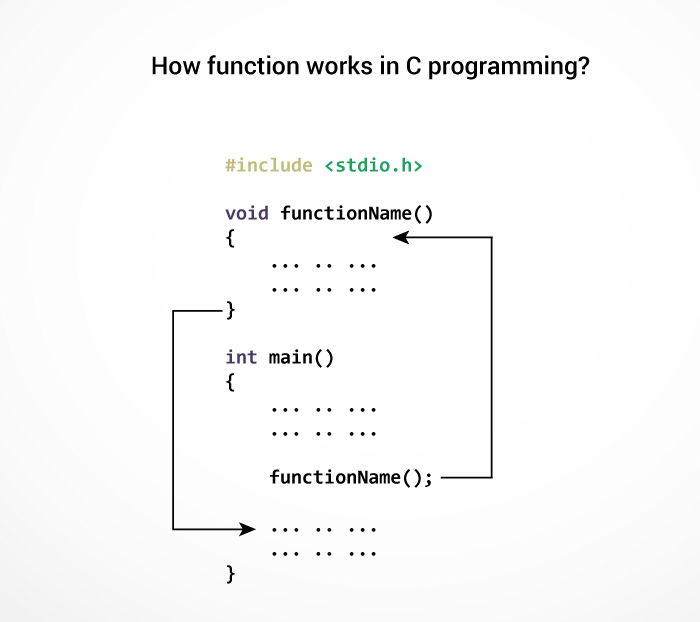
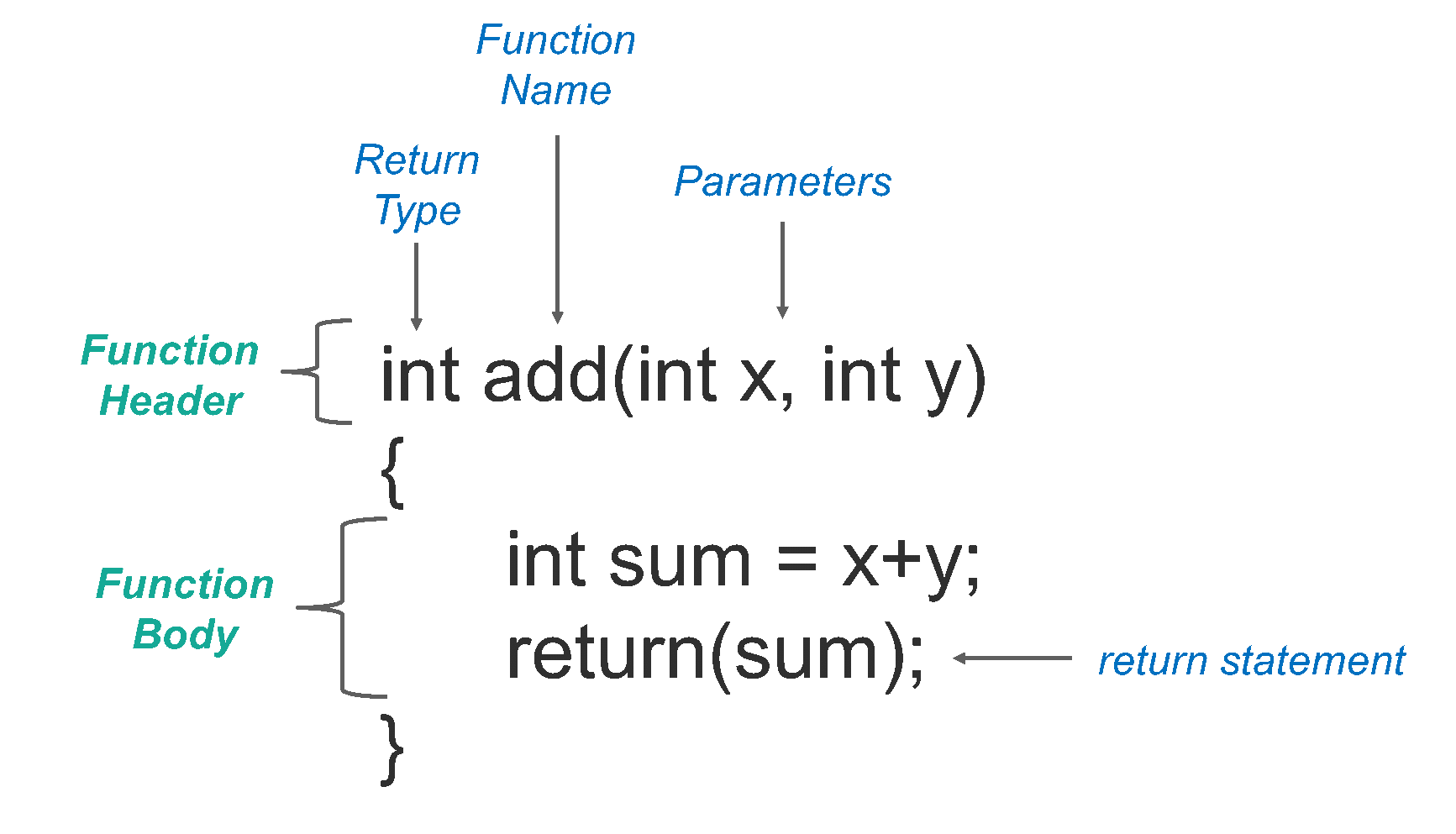
C programming tutorials for Beginners C Functions
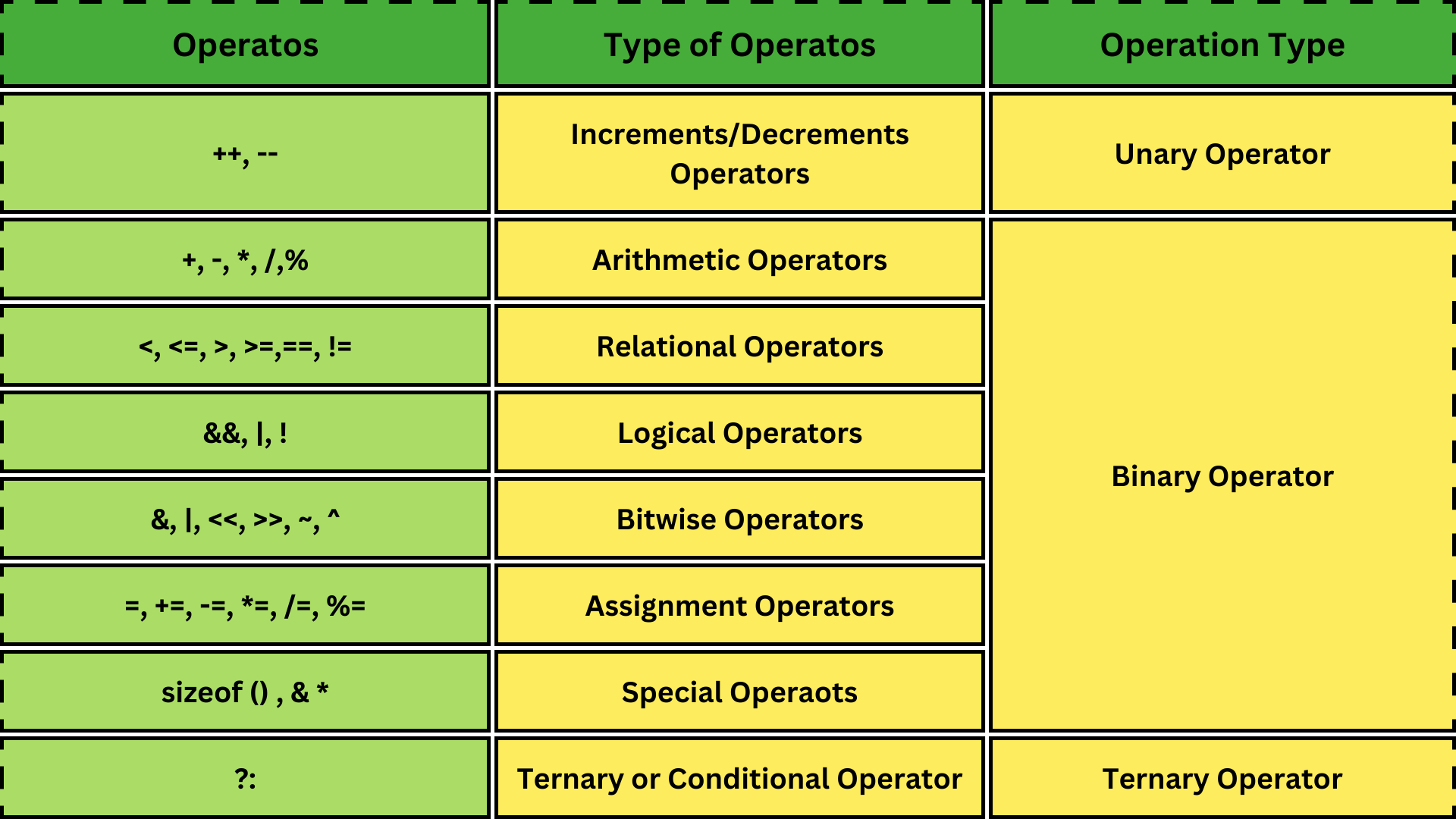
C++ Video Course (Hindi & English) Operators are symbol which tells the compiler to perform certain operations on variables. For example, (*) is an operator which is used for multiplying two numbers. There are different types of operators in C. Let's take a look at each type of them with few examples of each.
Operators In C Logicmojo
In this article. The => token is supported in two forms: as the lambda operator and as a separator of a member name and the member implementation in an expression body definition.. Lambda operator. In lambda expressions, the lambda operator => separates the input parameters on the left side from the lambda body on the right side.. The following example uses the LINQ feature with method syntax.

C Programming Tutorial 21 The Logical AND Operator YouTube
In C, this operator enables the programmer to access the data elements of a Structure or a Union. This operator (->) is built using a minus (-) operator and a greater than (>) relational operator. Moreover, it helps us access the members of the struct or union that a pointer variable refers to. Let us now focus on the structure of Arrow.

define in C Example Made Easy Lec 88 Learning Monkey
3. The * in declaration means that the variable is a pointer to some other variable / constant. meaning it can hold the address of variable of the type. for example: char *c; means that c can hold the address to some char, while int *b means b can hold the address of some int, the type of the reference is important, since in pointers arithmetic.
Functions In C Programming C fundamentals Edureka
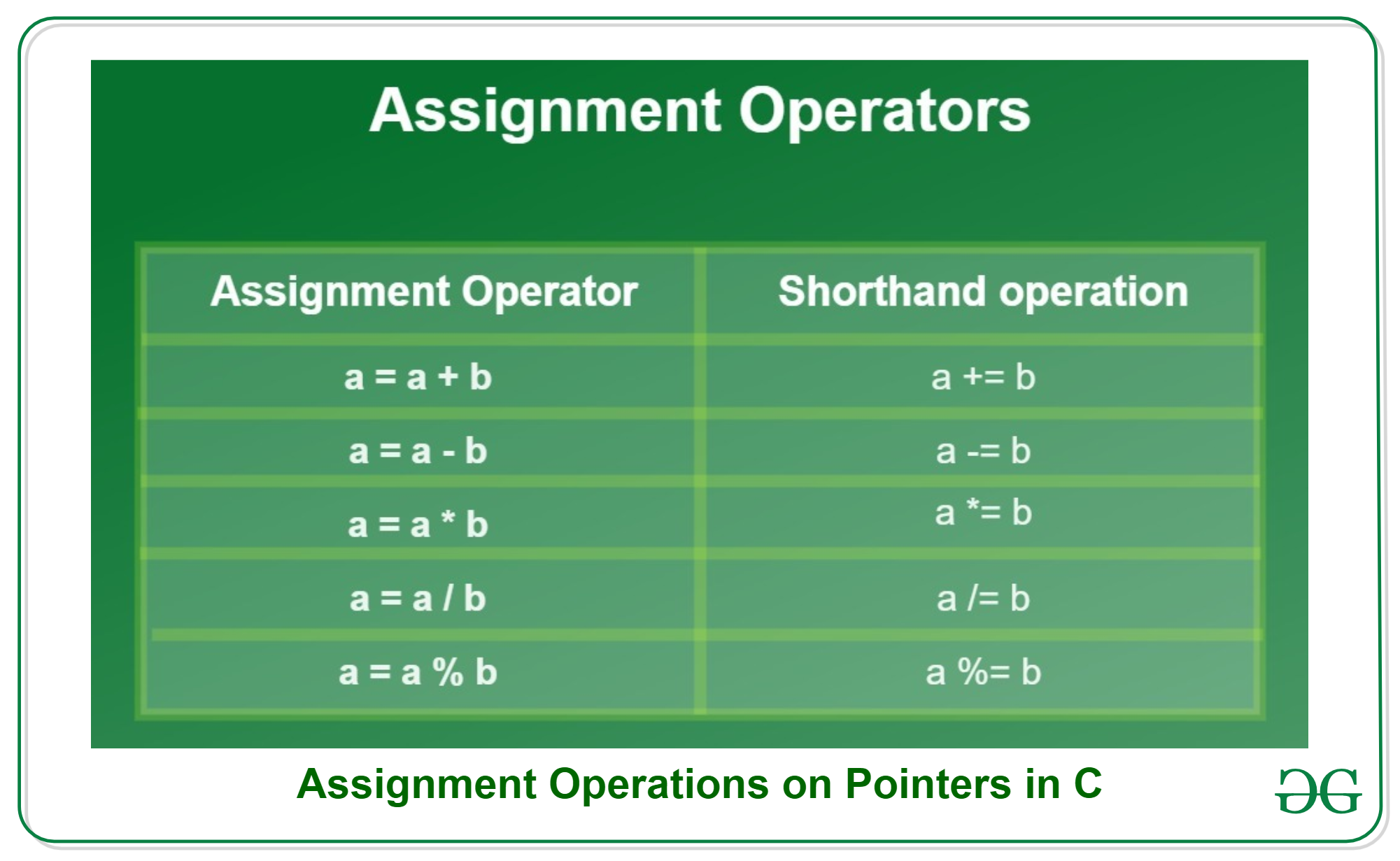
This program prints on screen the final values of a and b (4 and 7, respectively). Notice how a was not affected by the final modification of b, even though we declared a = b earlier. Assignment operations are expressions that can be evaluated. That means that the assignment itself has a value, and -for fundamental types- this value is the one assigned in the operation.

Functions in C YouTube
The C language supports a rich set of built-in operators. An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform a certain operation (arithmetic, comparison, etc.) using the values provided along with the operator.. Operators are used in programs to manipulate data and variables. Before moving forward with Operators in C language, we recommend you learn about C variables and datatypes:
Pointer Expressions in C with Examples
In C or C++, the modulo operator (also known as the modulus operator), denoted by %, is an arithmetic operator. The modulo division operator produces the remainder of an integer division which is also called the modulus of the operation. Syntax of Modulus Operator. If x and y are integers, then the expression:
[Solved] What does mean in C++? 9to5Answer
It is shifting the number 1 to the left 0 bits, which is equivalent to the number 1. It is commonly used to create flags, numbers that can be combined together with | (bit or) and various operations can be applied to them, such as testing whether a flag is set, setting a flag, removing a flag, etc. The reason that they can be combined together.

Pointer Expressions in C with Examples
This is a list of operators in the C and C++ programming languages.All the operators (except typeof) listed exist in C++; the column "Included in C", states whether an operator is also present in C. Note that C does not support operator overloading.. When not overloaded, for the operators &&, ||, and , (the comma operator), there is a sequence point after the evaluation of the first operand.

Basic Structure OF C Program with Example
Stringizing operator (#) The stringizing operator (#) is a preprocessor operator that causes the corresponding actual argument to be enclosed in double quotation marks. The # operator, which is generally called the stringize operator, turns the argument it precedes into a quoted string.It is also known as the stringification operator. It is generally used with macros in C.

Type Conversion in C
335. The dot (.) operator is used to access a member of a struct, while the arrow operator ( ->) in C is used to access a member of a struct which is referenced by the pointer in question. The pointer itself does not have any members which could be accessed with the dot operator (it's actually only a number describing a location in virtual.
C Tutorials data types in C Programming Language
The output of bitwise AND is 1 if the corresponding bits of two operands is 1. If either bit of an operand is 0, the result of corresponding bit is evaluated to 0. In C Programming, the bitwise AND operator is denoted by &. Let us suppose the bitwise AND operation of two integers 12 and 25. 12 = 00001100 (In Binary) 25 = 00011001 (In Binary)

C Programming Userdefined functions
An operator in C can be defined as the symbol that helps us to perform some specific mathematical, relational, bitwise, conditional, or logical computations on values and variables. The values and variables used with operators are called operands. So we can say that the operators are the symbols that perform operations on operands.
