
99.9 Pure Copper T2 Cu Metal Sheet Foil 0.011mm Sheet Copper Roll 100cm Long eBay
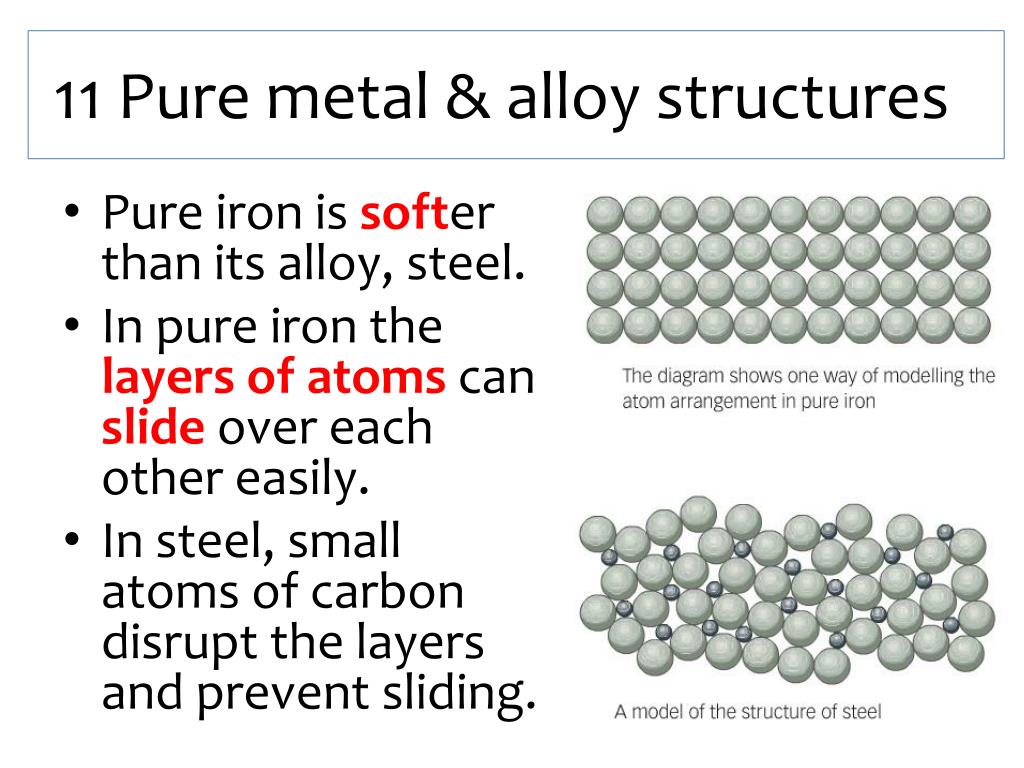
In a pure metal, the force needed to make the layers slide over each other is small. This explains why many pure metals are soft. In an alloy, there are atoms of different sizes.

10 Strongest Metals in the World 10 is out of this world
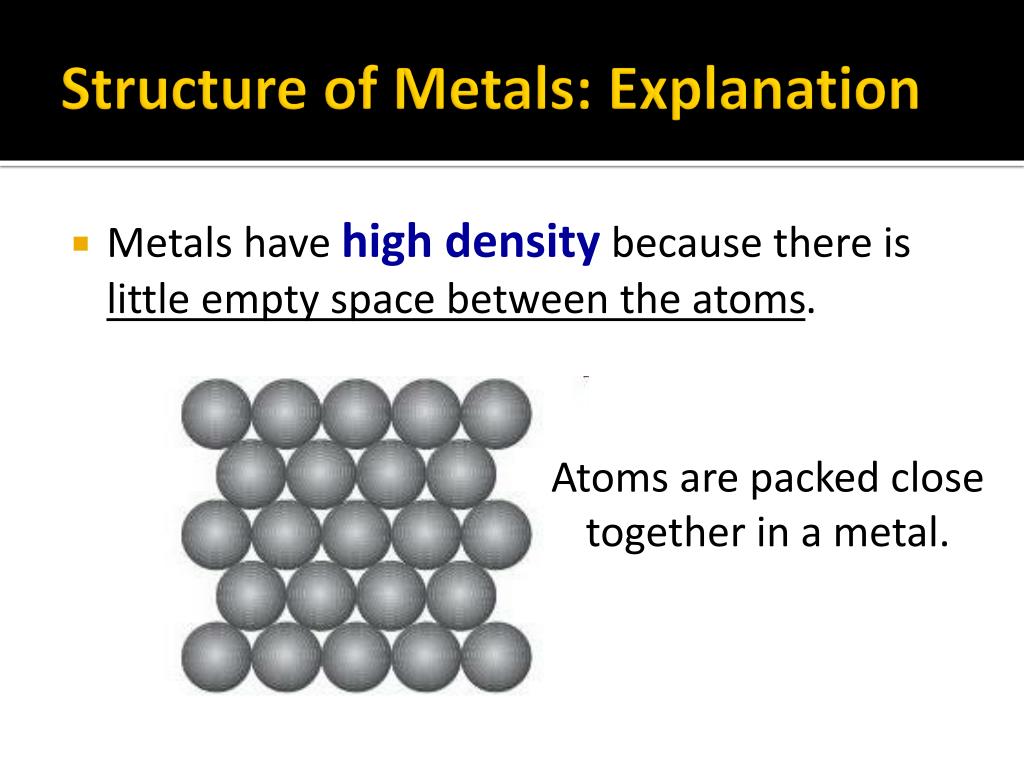
Pure Metals. In general, metals have the following physical properties: Usually have high densities. Malleable and ductile. Usually have high melting points and boiling points i.e. exists as solids at room temperature. Good conductors of electricity (and heat) These physical properties can be easily explained by looking at the structures of metal.

Pure Metals N.T. Ruddock Company
Chemical Composition. By definition, pure metals consist of a single element. Samples of these metals contain nothing but atoms of a single metallic substance. Alloys contain two or more elements or alloys melted and blended together, so their chemical formulas consist of more than one element. For example, the pure metal iron consists only of.

Alloys Edexcel 91 Separate (Triple) Science Teaching Resources
Mixtures of metals, called alloys, are more commonly used than the pure metal. By alloying, some of the important properties of metals can be improved. Solder, which is used in the electronics industry, is a mixture of tin and lead. One type of solder (63% tin and 37% lead) has a lower melting point but is harder than either of the metals.

Iron Metal 99.99 Pure 10 Grams Element Collection Amazon.co.uk Home & Kitchen
The pure metal is second only to silver in thermal and electric conductivity. Copper is commercially produced mainly by smelting. Copper, a chemical element that is a reddish, extremely ductile metal and an excellent conductor of electricity and heat. The pure metal is second only to silver in thermal and electric conductivity.

What Is an Alloy? Definition and Examples
The purest you can get in jewelry is 24 karats, which is about 99.7% pure gold. Gold can also be mixed with other metals to change its color; white gold, which is popular for jewelry, is an alloy of gold and platinum or palladium. Metal from Ore. Ores are rocks or minerals from which a valuable substance - usually metal - can be extracted.

13 Best Examples of Pure Substances [Simple Explanation] RankRed
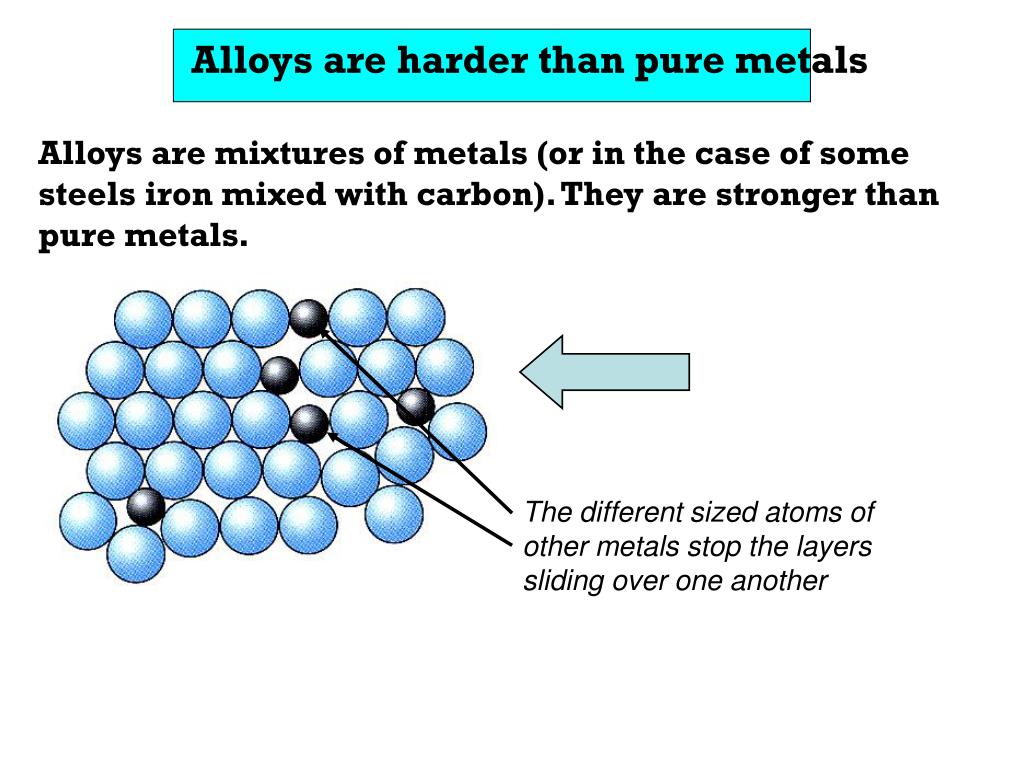
The primary difference between alloy and pure metal is that an alloy is a mixture of two or more metals, while a pure metal is made up of only one type of element. Alloys are usually created in order to combine the desirable characteristics of each component material into one product. For example, steel is an alloy made up primarily of iron and.
/GettyImages-dor75018979-56a133ac5f9b58b7d0bcfd73.jpg)
List of Platinum Group Metals or PGMs
H ard, shiny, and tough—metals are the macho poster boys of the material world. Learning how to extract these substances from the Earth and turn them into all kinds of useful materials was one of the most important developments in human civilization, spawning tools, jewelry, engines, machines, and giant static constructions like bridges and skyscrapers.
PPT Metals PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6413590
Metal atoms differ from nonmetal ones in how well they steal valence electrons from other atoms. One might say that metals are bad thieves. Instead of capturing a neighbor's electrons, they usually give up their own. This tendency to lose electrons is described as their "metallic character.".

PURE METAL, ALLOYS AND SUPERCONDUCTORS BEGINNERS GUIDE (IGCSE & SPM) YouTube
metal, any of a class of substances characterized by high electrical and thermal conductivity as well as by malleability, ductility, and high reflectivity of light. Approximately three-quarters of all known chemical elements are metals. The most abundant varieties in the Earth's crust are aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
PPT 1 Elements and their atoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2055155
What is the Solidification of Pure Metals. The solidification of a pure metal begins with the heating of the metal above its melting point, causing it to become a liquid. As the molten metal cools, the thermal energy is gradually dissipated, and the atoms lose kinetic energy, leading to a decrease in atomic mobility.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/155422145-56a613e15f9b58b7d0dfcc65.jpg)
The Properties and Uses of Zinc Metal
A metal (from Ancient Greek μέταλλον (métallon) 'mine, quarry, metal') is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the metallic bond.

Metals
Aluminum metal packs in a cubic closest-packed structure in which one plane of atoms can slip past another. As a result, pure aluminum metal is too weak to be used as a structural metal in cars or airplanes. Precipitation hardening produces alloys that are five to six times as strong as aluminum, and make an excellent structural metal.

Iron Powder Various Application Uses for This Versatile Powdered Metal
Exercise 2.1.1 2.1. 1. An alloy is a mixture of two metals. Steel is an alloy of iron with any of a number of other elements, such as chromium or vanadium. Alloys are often harder than metals composed of a pure element. Show how alloying introduces a defect into the metal, and how that makes the metal stronger. Answer.

World's 10 most precious metals
Differences in Properties. There are several key differences in the properties of alloys and pure metals: Strength: Alloys are generally stronger than pure metals due to the addition of other elements that create a more robust atomic structure. Hardness: Alloys tend to be harder than pure metals, making them more resistant to wear and deformation.
PPT Metals PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3827489
Tantalum (Ta) is a rare, blue-gray metal with a high level of purity, up to 99.9%. It's corrosion-resistant, ductile and has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. It's commonly used in capacitors, foil and high-power resistors and as an alloying element. Titanium. Titanium is a versatile metal with 3 commercially pure grades: 1, 2.
- Flights From Orange Nsw To Sydney
- Working Week In Abu Dhabi
- 29 Wentworth Street Point Piper
- Heart Island Alexandria Bay Ny
- How To Say Joaquin Phoenix
- What Is The Difference Between And
- Catholic Church Gold Coast Australia
- Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles Svg
- How Do You Resell Tickets
- Best Western Inn Carlton Melbourne
