
Mrp Maximum Retail Price Acronym Business Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 1797585772 Shutterstock
Maximum retail price. The MRP of this bottle of water in Sri Lanka is 90 Rupees. Maximum retail price ( MRP) is a manufacturer-calculated price that is the highest price that can be charged for a product sold in India, Indonesia, where it is known as Harga Eceran Tertinggi ( HET ), and Bangladesh. [1] The MRP is also imposed by the government.
Maximum prices definition, diagrams and examples Economics Help
Maximum Retail Price (MRP) is a retailing concept practiced in some markets, such as India, where merchandise is shipped from the manufacturer to the store with the final retail price of the item (including all taxes) printed on the item package. This protects customers from being charged a higher price, or an additional charge, by the retailer.
Education resources for teachers, schools & students EzyEducation
One way is to use the Retail Price Formula. This formula looks like this: Retail Price = Markup + Cost of Goods. Cost of Good = Retail Price — Markup. Markup = Retail price — Cost of Goods. He can also use an online Retail Price Calculator to do the math for him.

MRP Maximum Retail Price Acronym Stock Image Image of india, shop 250145207
Retail Price = Cost Price + Markup Amount = $10 + $4 = $14. It's important to note that this is a simplified formula, and more complex pricing models might be used in practice, considering factors like discounts, variable costs, and competitor pricing.

Comparison between Unit Price and Maximum Retain Price
NIST SP 1181: Unit Pricing Guide "A Best Practice Approach to Unit Pricing" (2015) Currently, nineteen (19) states and two (2) territories have unit pricing laws or regulations in force. Eleven (11) of these have mandatory unit pricing provisions. They are: Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oregon.

MRP Maximum Retail Price Acronym Stock Image Image of marker, 197897671
EU and UK competition law generally prohibits an arrangement between a retailer and a supplier under which the retailer agrees to resell goods or services at a price: that is fixed (directly or indirectly) by the supplier or above a minimum price level set by the supplier; which has been agreed between the supplier and the retailer; or.

PPT Retail Pricing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4792684
Maximum Retail Price (MRP) is generally determined by the manufacturer or seller of the product. It is the highest price at which the product can be sold to the end consumer, and includes all taxes. The MRP is based on various factors such as production costs, marketing expenses, and profit margin. The manufacturer or seller will consider these.
Maximum prices definition, diagrams and examples Economics Help
Conclusion Regarding Retail Price. The price that a consumer will pay for a product while purchasing at a retail store is referred to as the retail price of that product. This is the total amount that a customer will be charged. The amount a consumer pays for a finished good at a retail establishment is the retail price.

MRP Maximum Retail Price Acronym, Business Concept Background Stock Illustration
MRP (Maximum Retail Price) is the highest price at which a product can be legally sold to consumers, including all taxes and charges. In contrast, a fixed price is a predetermined, non-negotiable cost for a product or service.

Maximum Retail Price Text on Blackboard Stock Photo Image of bangladesh, sell 197902204
What is the Maximum Retail Price (MRP)? The Maximum Retail Price (MRP) represents the upper limit at which a product can be sold, aligning with the manufacturer's or distributor's recommended pricing and encompassing all applicable taxes.

Good To Know The Difference Between Maximum Retail Price & Market Operating Price
Maximum Retail Price (MRP) under GST: A Comprehensive Guide. Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive tax structure that was implemented in India on 1st July 2017. Under GST, several taxes, including Value Added Tax (VAT), Service Tax and Excise Duty, were merged into a single tax system. One of the key aspects of GST is the Maximum.
Maximum prices definition, diagrams and examples Economics Help
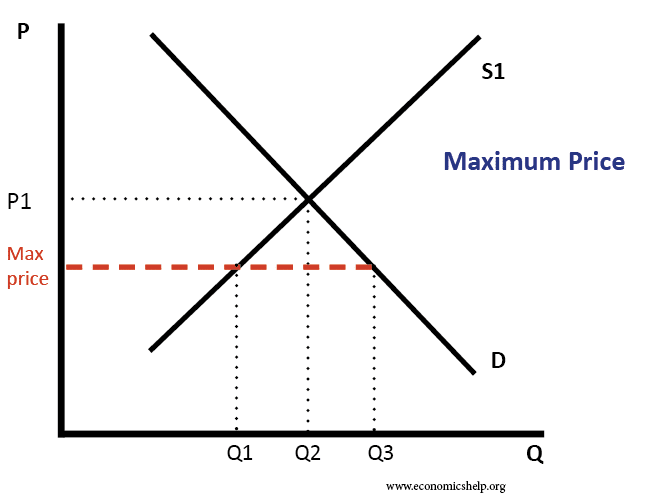
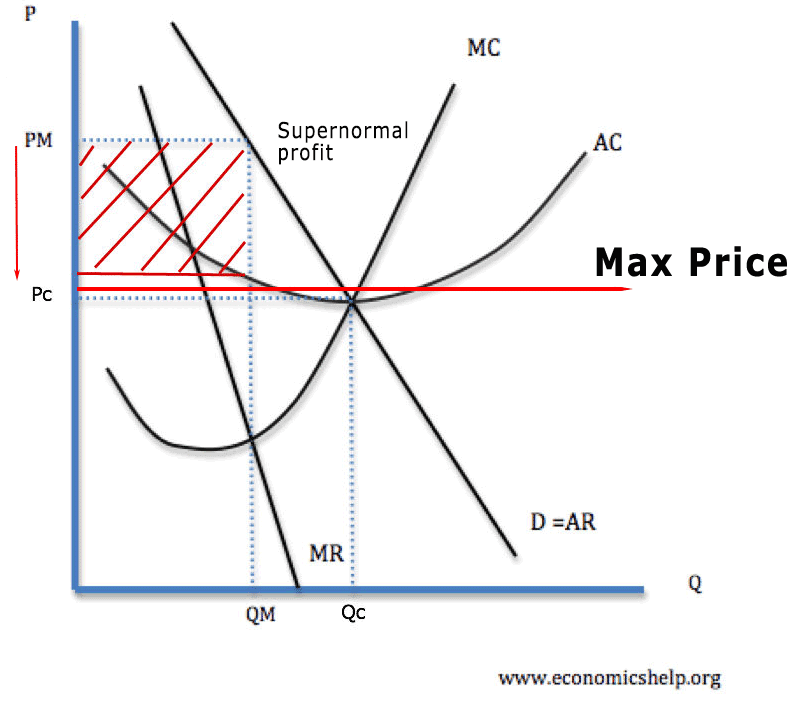
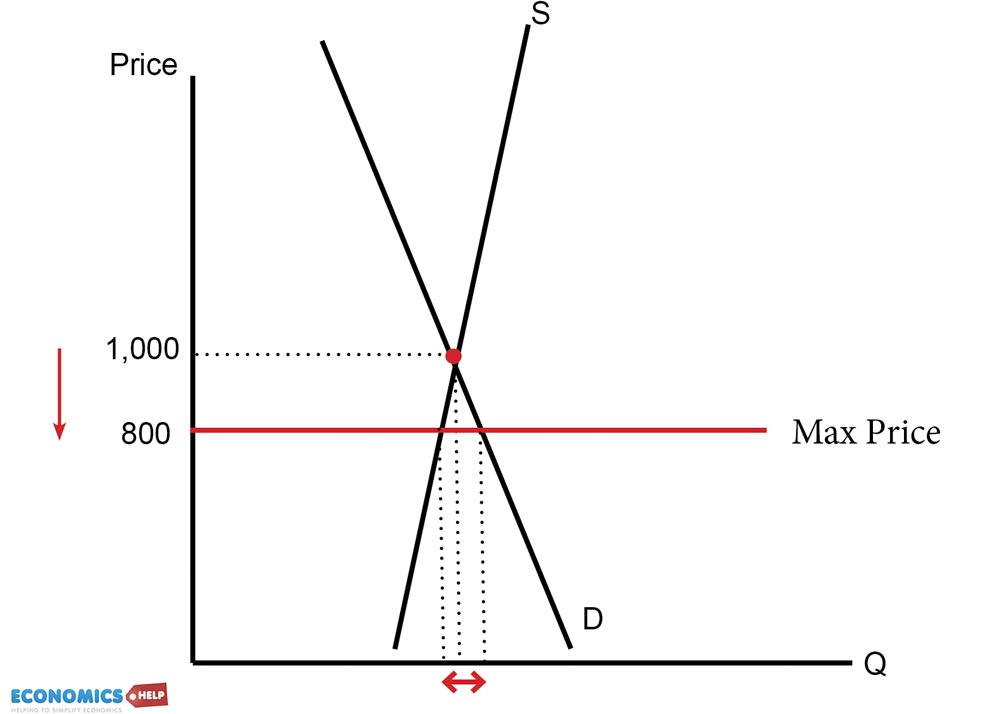
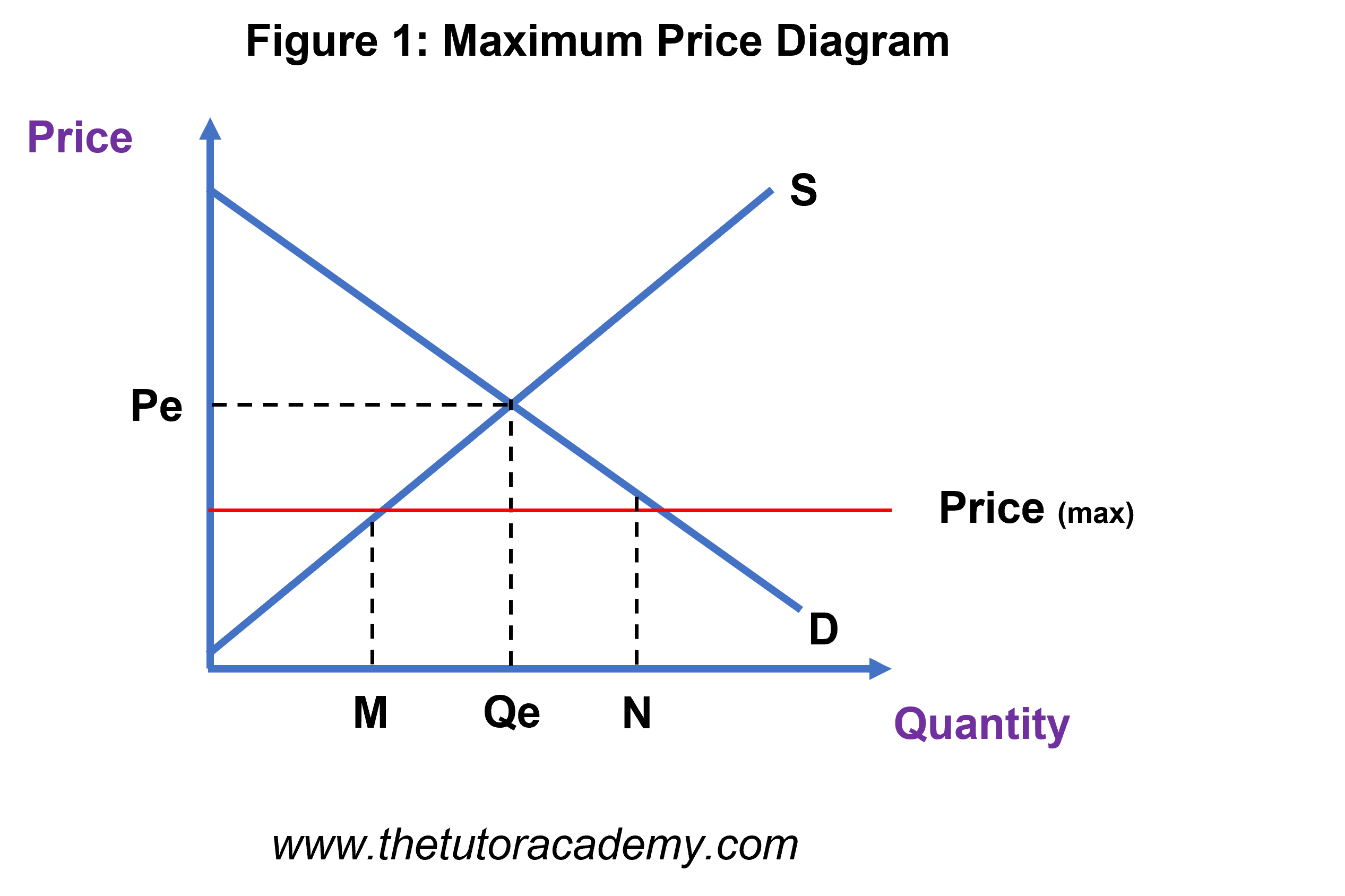
Definition - A maximum price occurs when a government sets a legal limit on the price of a good or service - with the aim of reducing prices below the market equilibrium price. For example, the government may set a maximum price of bread of £1 - or a maximum price of a weekly rent of £150. If the maximum price is set above the.

MRP Maximum Retail Price Acronym, Business Concept on Blackboard Stock Photo Image of
The full form of MRP is Maximum Retail Price, which refers to the cost of products and services determined by the manufacturer itself. This price is the highest possible price that can be quoted for an item. This pricing system includes all taxes levied on that product and is common in nations like India and Bangladesh.
Maximum Prices (Price ceilings) Economics Revision The Tutor Academy The Tutor Academy
The change in maximum retail price cannot be more than the net price increase of the product because of tax. For example, Old MRP Rs 100. Increase in the tax amount due to rate change - Rs 10. New MRP - Cannot be more than Rs 110. Only the stocked products with the manufacturer were required to put on the advertisement.
MRP maximum retail price. acronym business concept. vector illustration concept with keywords
Retail Price = COGS / (1 - Margin Percentage) For a COGS of $50 and a desired 50% margin: Retail Price = $50 / (1 - 0.50) = $100.. This strategy is commonly used in e-commerce and allows retailers to optimize prices for maximum profitability. Dynamic pricing requires access to real-time data and advanced pricing algorithms.

Text mrp hires stock photography and images Alamy
💰 Maximum retail price (MRP) MRP, or maximum retail price, is actually set by the government or industry regulators. It designates the maximum price you can sell a product for. For example, MRP might dictate that you can't sell toilet paper to customers for more than $20 a pack.
- The Cumberland Hotel London Uk
- Parking At International Convention Centre Sydney
- Countries With Yellow And Blue Flags
- Olympique Lyonnais Féminin Vs Fc Nantes Féminines Stats
- Suncorp Netball Grand Final Tickets
- Is Ascorbic Acid In Bread Bad For You
- Is The Lottery Office Legal In Australia
- The Biggest Stuff In The World
- Central To Penrith Train Timetable
- Middlesbrough F C Vs Ipswich Town Lineups
